Figure 1.
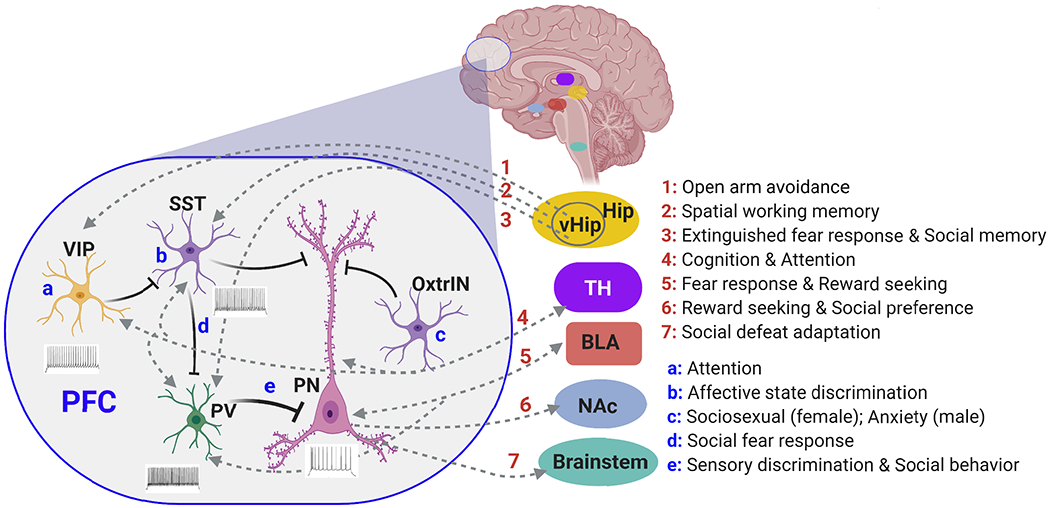
Plot of PFC organization highlighting the functional mapping of some long-range and local circuits of PFC. VIP+ interneurons (VIP) in PFC sends inhibitory inputs to SST+ interneurons (SST), which causes disinbition of PV+ interneurons (PV), resulting in the strong somatic inhibition and weak dendritic inhibition of pyramidal neurons (PN). PFC interneurons and PN are innervated by hippocampus (HIP) or ventral HIP (vHIP), thalamus (TH) and basolateral amygdala (BLA), while PN send output to TH, BLA, nucleus accumbens (NAc) and brainstem. Some behavioral correlates of these neuronal circuits are listed, along with the functional role of VIP+ or SST+ interneurons, as well as a subtype of SST+ interneurons expressing oxytocin receptor (OxtrIN).
