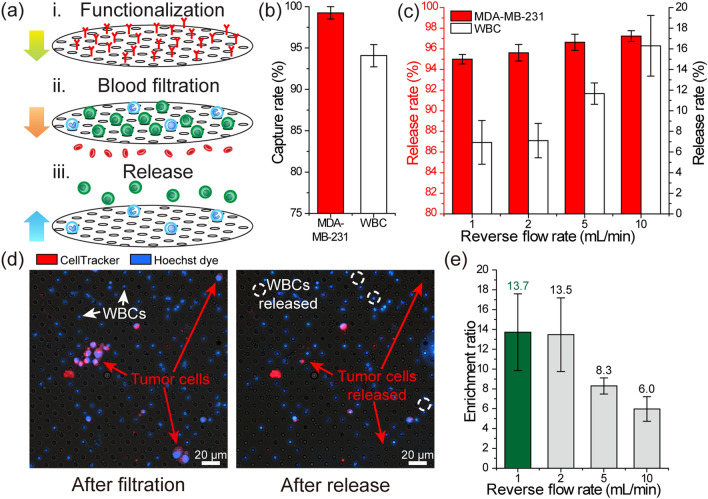
Figure 2.
Characterization of the immuno-functionalized PDMS membrane filter for tumor cell enrichment. (a) A schematic showing the tumor cell enrichment process. Following the immuno-functionalization of the membrane filter, whole blood spiked with MDA-MB-231 tumor cells is driven through the filter to capture nucleated cells on the filter and discard anucleated cells. The mechanically retained tumor cells are then released from the membrane filter under reverse flow. (b) Measured capture rates of the MDA-MB-231 tumor cells and WBCs during filtration (n = 3). (c) Measured release rates of the (left axis) MDA-MB-231 tumor cells and (right axis) WBCs under different reverse flow rates (n = 3). (d) Fluorescence microscope images of the PDMS membrane filter (left) right after the filtration of the blood sample and (right) following the release of cells under reverse flow. The images show that the tumor cells were succesfully released from the filter while most of the immunocaptured WBCs were retained on the filter with the reverse flow. (e) Calculated average enrichment ratio for the spiked tumor cells as a function of different reverse flow rates.