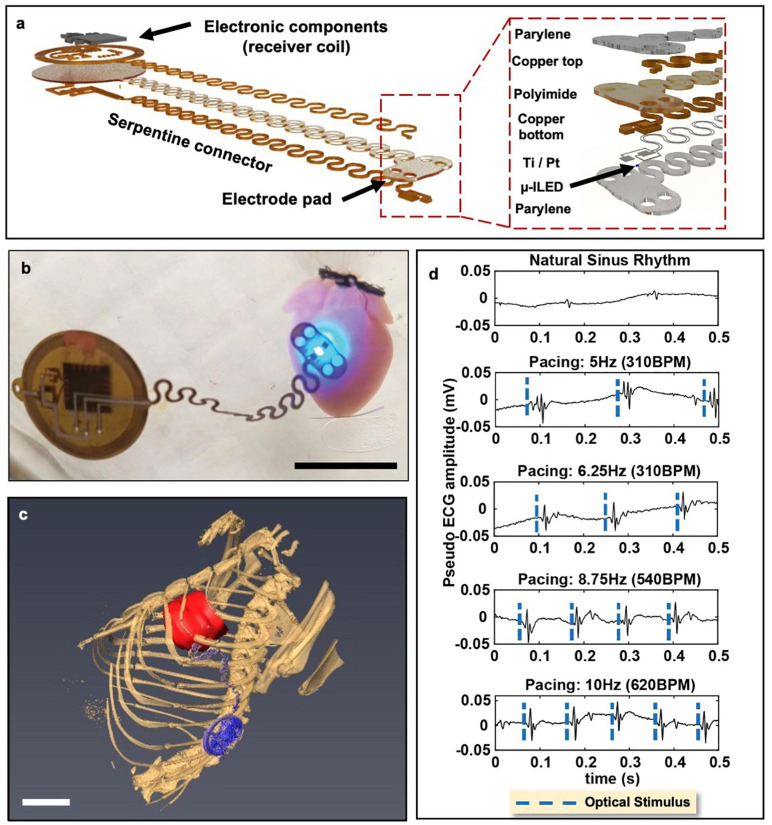
FIGURE 4.
Wireless, battery-free, full implantable optical pacemaker. (a) Rendered images of the layered composition of the miniature wireless optical pacemaker. The receiver coil receives energy to power the pacemaker. The electrode pad is placed onto the epicardium for pacing. (b) A representative image of the pacemaker performing optical pacing on a ChR2-expressing mouse heart. Scale bar, 1 cm. (c) 3D segmentation of anatomical positioning of the pacemaker (blue) with respect to the rat heart (red). Scale bar, 1 cm. (d) Ex vivo ChR2-expressing mouse hearts were paced at 280 BPM, 310 BPM, 540 BPM, and 600 BPM. Adapted from Gutruf et al. (2019).