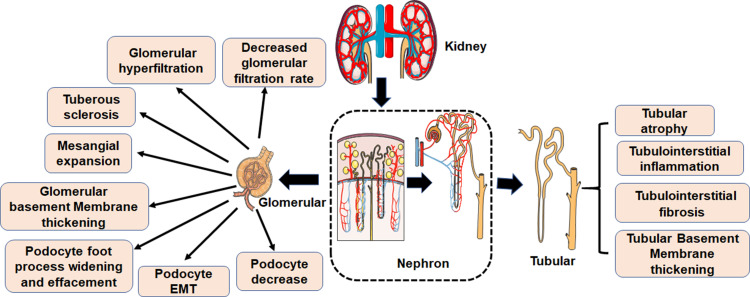
Figure 2.
Pathological characteristics of DN. The first clinical manifestation of classical DN is the increase of urinary albumin excretion. The glomerular filtration rate is normal or even increased before urinary albumin excretion, but the glomerular filtration rate decreases after continuous urinary proteinuria, and eventually even developed into ESRD. And with increased urinary albumin excretion and an independent decline in glomerular filtration function, the patient’s risk of cardiovascular disease increases. According to the Tervaert classification of DN, the glomerular lesions of DN can be divided into four grades. I: Irregular thickening of the glomerular basement membrane was observed under an electron microscope. II: Mesangial hyperplasia and mesangial dilatation occur. III: There is at least one recognized tuberous sclerosis. IV: Advanced diabetic glomerulosclerosis of glomeruli.