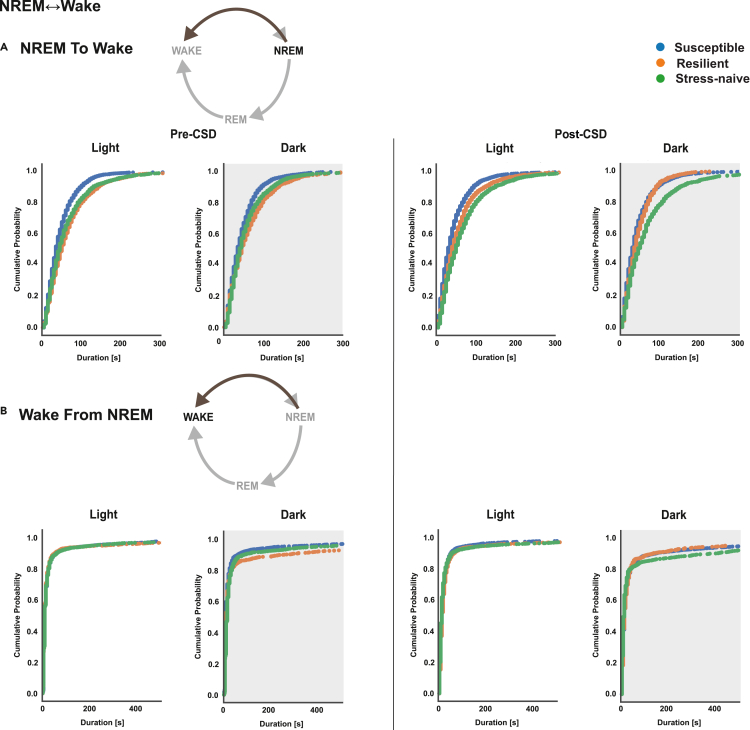
Figure 1.
NREM bouts in NREM↔Wake are shorter in duration in susceptible mice compared to resilient and stress-naïve mice in the light and dark, while wake bouts of susceptible mice are shorter in the dark pre- and post-CSD
(A) NREM: Pre-CSD: Susceptible mice exhibited significantly shorter NREM bouts duration in NREM↔Wake compared with resilient and stress-naïve mice in the light and the dark (p < 0.05 for both). Post-CSD: Light: Susceptible mice exhibit significantly shorter NREM bouts duration in NREM↔Wake compared with resilient and stress-naïve mice (p < 0.05 for both). Resilient mice have shorter NREM bouts, in NREM↔Wake, compared with stress-naïve mice (p < 0.05). Dark: Susceptible mice exhibit shorter NREM bout durations in NREM↔Wake compared with resilient and stress-naïve mice (p < 0.05 for both).
(B) Wake: Susceptible mice exhibit shorter wake bouts in NREM↔Wake compared to resilient and stress-naive mice in the dark pre-CSD. Stress-naïve mice exhibit longer wake bouts in NREM↔Wake compared to susceptible and resilient mice in the dark post-CSD. Pre-CSD: Light: the duration of wake bouts in NREM↔Wake was comparable between phenotypes. Dark: Wake bouts in NREM↔Wake in susceptible mice are shorter than in resilient and stress-naïve mice (p < 0.05 for both). Post-CSD: Light: the duration of wake bouts in NREM↔Wake was comparable between phenotypes. Dark: Wake bouts in NREM↔Wake in stress-naive mice are longer than in susceptible and resilient mice (p < 0.05 for both). Values are pooled individual bouts duration within each phenotype in the light and dark separately pre- and post-CSD. p values are computed via bootstrap method and Bonferroni-corrected for multiple comparisons. N = 7-8 for each group.