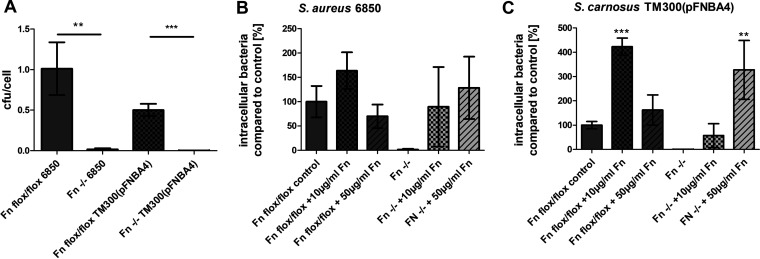
FIG 3.
Bacterial uptake is low in Fn null fibroblasts compared to control mouse fibroblasts; large amounts of Fn in culture medium enhance bacterial uptake in Fn null fibroblasts but not in control cells. (A) Fn1flox/flox mouse fibroblasts (Fn flox/flox) and Fn1−/− fibroblasts (Fn−/−) were infected with S. aureus 6850 or S. carnosus TM300(pFNBA4). One hour post infection, extracellular staphylococci were removed by lysostaphin treatment. Subsequently, the host cells were detached and the number of host cells was determined. Host cells were lysed and number of viable intracellular bacteria was assessed by plate counting. Data are means ± SD from three independent experiments. Bacterial uptake of one bacterial strain into the two different fibroblasts cell lines was compared. **, P < 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001, unpaired t test. (B and C) Culture medium of Fn1flox/flox fibroblasts and Fn1−/− fibroblasts was supplemented with Fn at the indicated concentrations. Cells were grown for at least 2 days to reach confluence. Cells were infected for 1 h with either S. aureus 6850 (B) or S. carnosus TM300(pFNBA4) (C). Extracellular staphylococci were removed by lysostaphin treatment. Subsequently, the host cells were detached and the number of host cells was determined. Host cells were lysed and the number of viable intracellular bacteria was assessed by plate counting. Numbers of intracellular bacteria in control cells were set to 100%. Data are means ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test.