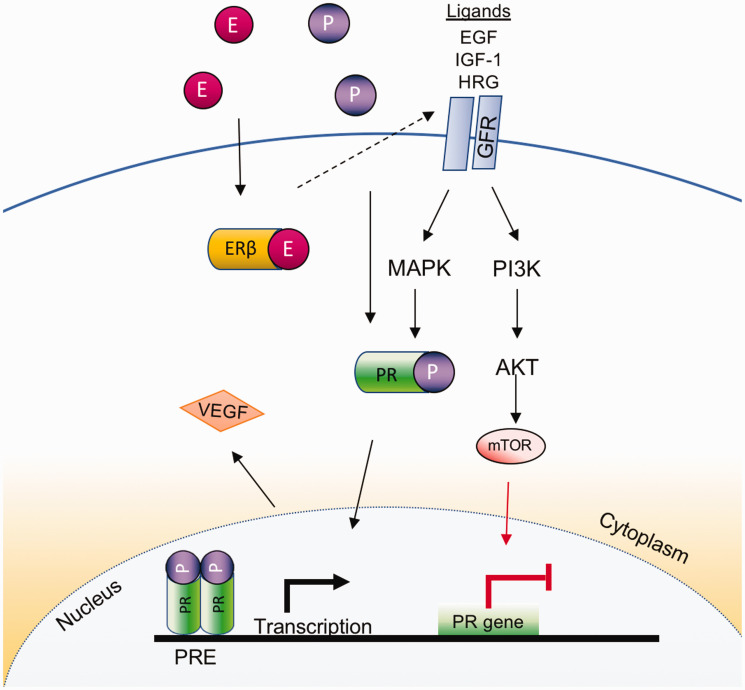
Figure 4.
Progesterone/progesterone receptor signaling in lung cancer. The growth factor receptor signaling is stimulated by its ligands (e.g. EGF, IFG-1, HRG), resulting in the activation of MAPK-related pathways and the subsequent stimulation of both (1) the ligand independent receptor activation and (2) the AKT/mTOR pathway, which increases and suppresses PR expression, respectively. In addition, estrogen and progesterone promote VEGF in lung cancer. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)
AKT: AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 1; E: estrogen; EGF: epidermal growth factor; ERβ: estrogen receptor β; GFR: growth factor receptor; HRG: histidine rich glycoprotein; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor 1; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinases; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin; P: progesterone; PI3K: phosphoinositide-3 kinase; PR: progesterone receptor; PRE: progesterone response elements; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor.