Fig. 5.
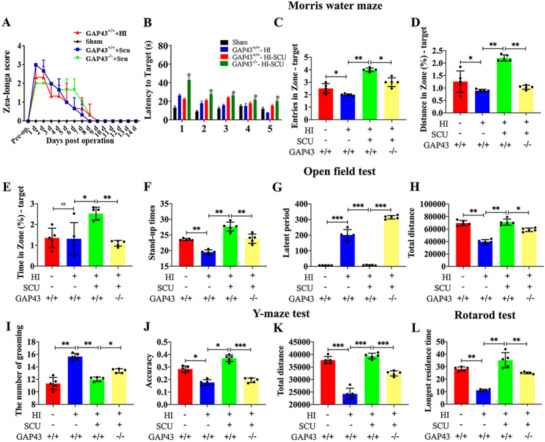
Role of GAP43 in long–term neurological function of Scu-treated HI rats. a Zea-longa scores of HI rats in the sham, GAP43+/+, GAP43+/+ + Scu, GAP43−/− + Scu groups. b The latency to target in these four groups in the Morris water maze test, respectively. c–e The number of crossing original location of platform and the distance and time for crossing the original location of quadrant in the GAP43+/+, GAP43+/+ + HI, GAP43+/+ + HI + Scu, GAP43−/− + HI + Scu groups. f, i The stand-up times and the number of grooming in the open field test in these groups. g, h The latent period and total distance in the open field test among the four groups. j, k The proportion of food arm entries and total distance finding the food arm of Y-maze in the above-mentioned groups. l The longest residence time in Rotarod test among these groups. GAP43+/+ wild-type rats; GAP43−/− GAP43 knockout, HI hypoxia–ischemia, Scu Scutellarin, d days. *p < 0.05 vs. GAP43+/+ + HI + Scu, **p < 0.01 vs. GAP43+/+ + HI + Scu, ***p < 0.001 vs. GAP43+/+ + HI + Scu, n = 5/group
