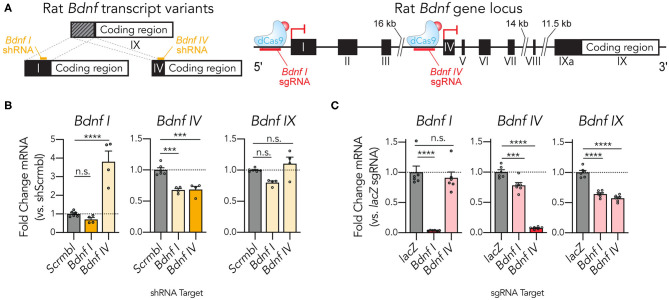
Figure 3.
dCas9-KRAB-MeCP2 induces targeted transcript specific Bdnf gene repression in primary rat hippocampal cultures. (A) Complex structure of the rat Bdnf gene produces spliced transcripts from multiple promoter regions using non-coding exons (I-IXa) and a common coding exon (IX). shRNAs (left) or sgRNAs (right) can be designed for targeted transcript suppression. (B) shRNA targeting the Bdnf I variant did not significantly decrease its expression as assessed by RT-qPCR, while shRNA designed against the Bdnf IV variant increased expression of the Bdnf I variant [left, Bdnf I RT-qPCR: n = 4–6, One-Way ANOVA, F(2,11) = 32.55, p < 0.0001. Middle, Bdnf IV RT-qPCR: n = 4–6, One-Way ANOVA, F(2,11) = 25.19, p < 0.0001]. Targeting either variant did not alter the expression levels of total Bdnf as measured using qPCR primers designed for the Bdnf IX common coding region [right, Bdnf IX RT-qPCR: n = 4–6, One-Way ANOVA, F(2,11) = 7.266, p = 0.0097]. (C) Individual sgRNAs designed upstream of the Bdnf I and Bdnf IV exons recruit dCas9-KRAB-MeCP2 to induce transcript specific gene repression of the Bdnf I and Bdnf IV transcript variants as assessed by RT-qPCR. Both sgRNAs resulted in a significant decrease in total Bdnf IX expression [left, Bdnf I RT-qPCR: n = 6, One-Way ANOVA, F(2,15) = 41.87, p < 0.0001. Middle, Bdnf IV RT-qPCR: n = 6, One-Way ANOVA, F(2,15) = 181.9, p < 0.0001. Right, Bdnf IX RT-qPCR: n = 6, one-way ANOVA, F(2,15) = 74.56, p < 0.0001]. Tukey's multiple comparisons test was used for individual comparisons. All data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. Individual comparisons; ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.