Figure 1.
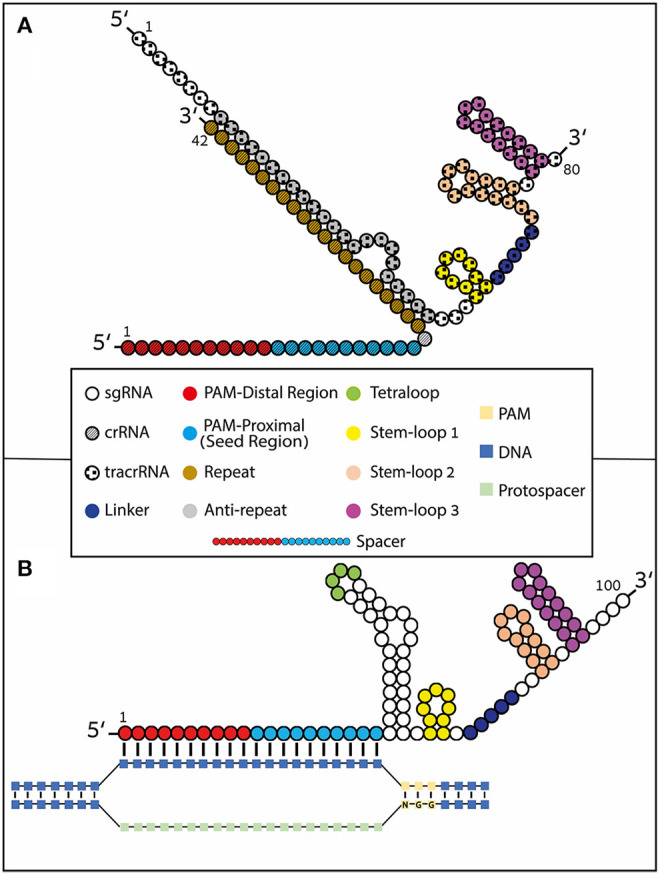
Type II CRISPR formulations. gRNAs contain 4 loop structures: tetraloop (green), Stem-loop 1 (yellow), Stem-loop 2 (orange), and Stem-loop 3 (magenta). Stem-loop 2 and tetraloop do not interact with Cas9 as they protrude from the nuclease (Konermann et al., 2015). The spacer region of the guide undergoes Watson and Crick base pairing with the complimentary stand to the DNA protospacer. The spacer region (also known as guide region) is typically 20 nucleotides long but it has been shown that it can be shortened or lengthened (to include hairpin structures) at the 5′ end. The spacer region can be divided into two regions: the PAM-proximal (seed) region and the PAM-distal region. (A) Naturally occurring crRNA [~42 nt (striped nucleotides)] containing the DNA-binding spacer sequence and the trans-activating tracrRNA [80 nt (Rahdar et al., 2015) (checkered nucleotides)] annealed together through Watson and Crick base-pairing by the repeat (brown) and anti-repeat (gray) regions. (B) Synthetic sgRNA formulation where the crRNA and tracrRNA are covalently fused by a tetraloop. R-loop formation is depicted with Watson and Crick base pairing of the RNA:DNA heteroduplex.
