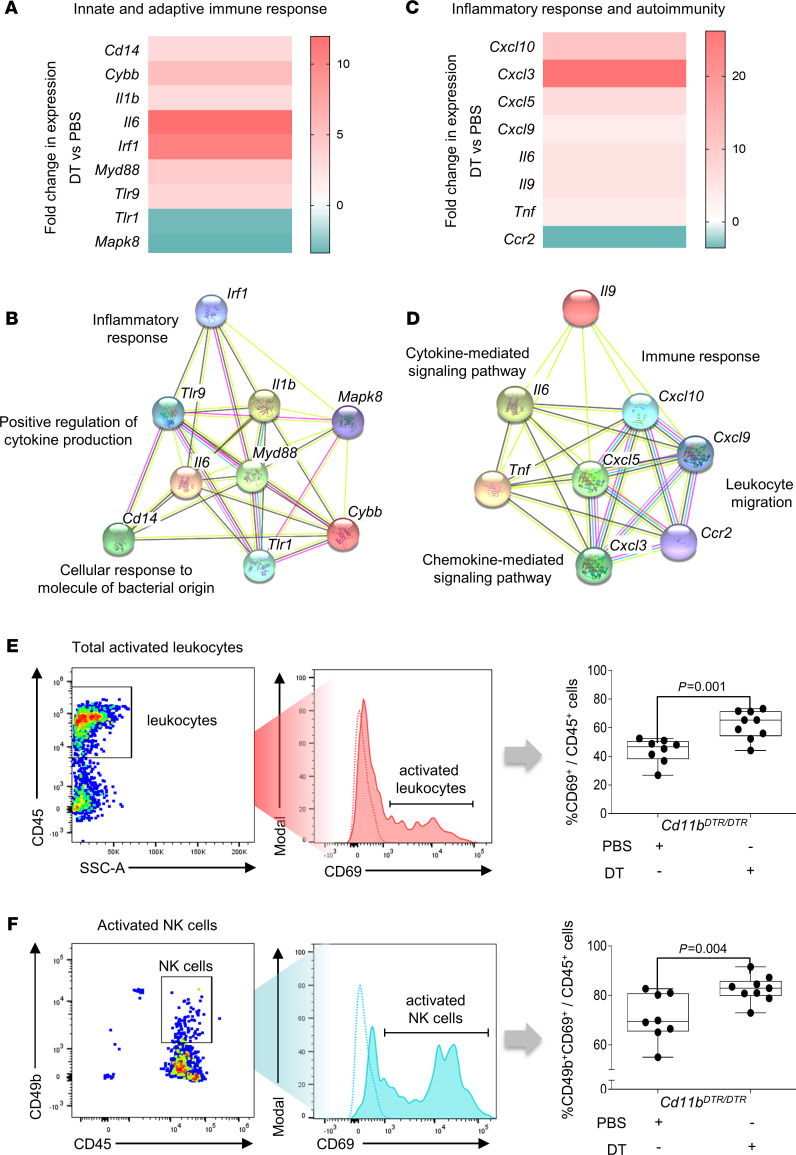
Figure 5. Depletion of maternal CD11b+ myeloid cells promotes upregulation of inflammatory mediators and leukocyte activation at the materno-fetal interface.
Cd11bDTR/DTR dams were administered diphtheria toxin (DT, 25 ng/g, i.p.) or PBS on 16 dpc. The uterine decidua was collected 24 hours later for gene expression profiling using RT-qPCR arrays (tissue pooled from n = 7–8 per group) and for analysis of leukocytes by flow cytometry (n = 7–8 per group). (A) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes and (B) interaction network obtained by STRING analysis of pathways attenuated in the decidua after depletion of CD11b+ cells, obtained using the “innate and adaptive immune response” array. (C) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes and (D) interaction network obtained by STRING analysis of pathways attenuated in the decidua after depletion of CD11b+ cells, obtained using the “inflammatory response and autoimmunity” array. Flow cytometry gating strategy for determining the effect of CD11b+ cell depletion on proportions of (E) activated leukocytes (CD69+/CD45+ cells) and (F) NK cells (CD49b+CD69+/CD45+ cells) in decidual tissues. Data are presented as box plots where the midline indicates the median, the box indicates the IQR, and whiskers indicate the minimum/maximum range. Symbols are values from individual dams. Data were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U tests. P values were considered significant when P was less than 0.05.