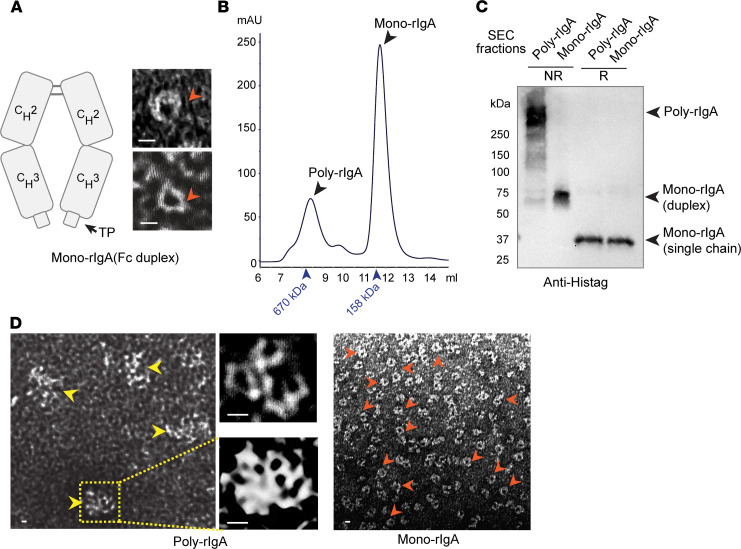
Figure 2. Intermolecular disulfide bond(s) involved in the self-aggregation of recombinant poly-rIgA.
(A) Recombinant human and rat IgA mimetics comprising the CH2-CH3-Tailpiece (TP) segment of IgA heavy chain. Similar to native IgA heavy chain, the mimetics form a duplex that is referred to as mono-rIgA. TEM images confirmed rat rIgA duplexes in donut-like appearances. (B) Rat rIgA was resolved by SEC with a clear separation of its poly- and mono-rIgA contents. (C) SDS-PAGE results confirmed the presence of disulfide connections among self-associated rIgA in poly-rIgA complexes (NR, nonreducing condition): Under reducing conditions (R), both poly- and mono-rIgA reduced to single chains of 32 kDa. (D) TEM images of poly-rIgA SEC fraction showed rIgA aggregates (left, yellow arrowheads). High-magnification images (middle) show structures with multiple circular voids of monomeric rIgA units, in contrast to mono-IgA, which appeared as single donut-like structures (red arrowheads). Scale bar: 10 nm. Other examples of TEM images are shown in Supplemental Figure 2.