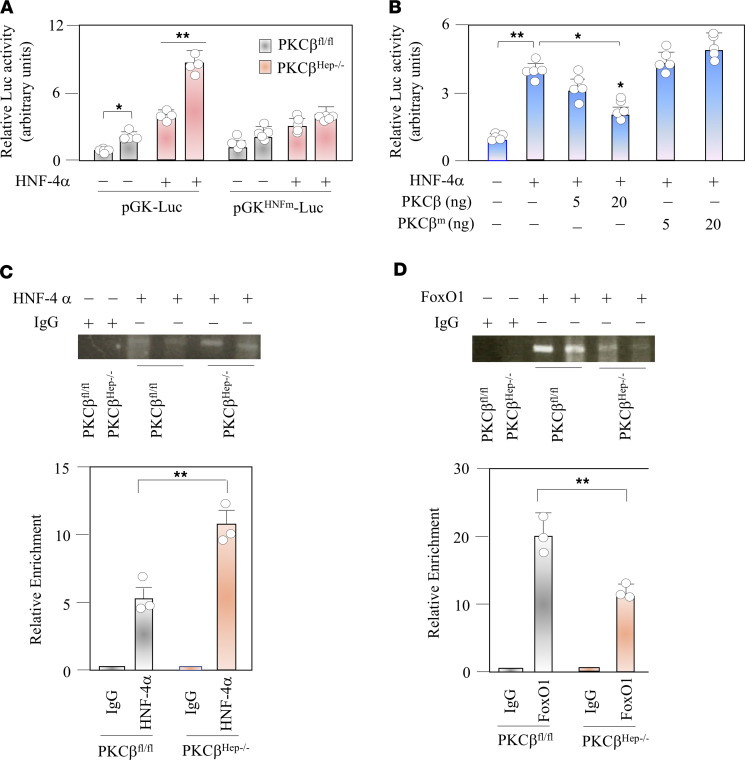
Figure 5. Hepatic PKCβ deficiency transactivates HNF-4α and promotes its occupancy while reducing FoxO1 occupancy at the GK promoter.
(A) PKCβfl/fl and PKCβHep–/– hepatocytes were transiently cotransfected with either WT pGK-Luc (300 ng) or HNF-4α site mutated reporter plasmid (pGKHNFm-Luc) construct (300 ng) with or without expression vector for human HNF-4α (50 ng). After transfection, cells were incubated in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS for 12 hours and then serum-starved for 9 hours in the presence or absence of 100 nM insulin. (B) HepG2 cells were cotransfected with pGK-Luc (100 ng) along with expression vector for human HNF-4 (20 ng) with or without human PKCβ expression. Transfected cells were treated with insulin as described above. In each experiment, luciferase activity was presented as fold change with respect to transfection of pGK-Luc reporter plasmid alone. The values represent mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (C and D) Binding of FoxO1 and HNF-4α were analyzed by ChIP assays with chromatin isolated from mice liver in the fed state. As a control, chromatin was immunoprecipitated with nonspecific IgG. Bound DNA was analyzed by PCR and images were quantified. Enrichment compared with input DNA was calculated. Results were normalized to precipitation using IgG in the fed state. Values are mean ± SEM for triplicates. *P < 0.05 for 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison test. **P < 0.01.