Figure 7.
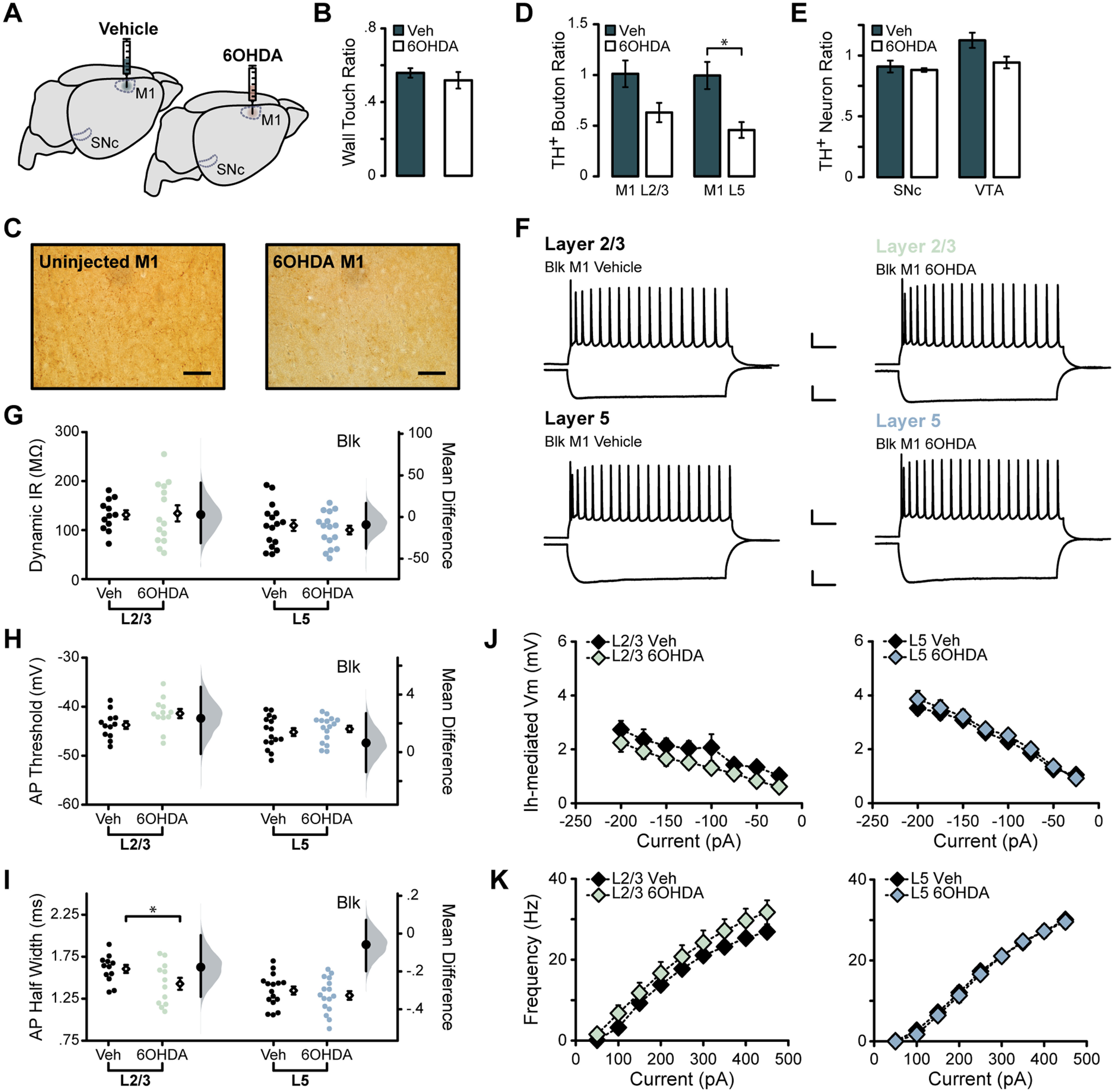
Chronic M1 dopamine depletion impacts L2/3 intrinsic excitability. A, Unilateral injection of 6OHDA or vehicle into forelimb region of M1. B, Quantification of weight-bearing wall touches in cylinder motor assessment. C, TH+ axons and boutons labeled in L2/3 of M1 ipsilateral and contralateral to the injection site. Magnification, 40×. Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Stereological counts of TH+ boutons in M1 in lesioned (N = 4) or vehicle-injected (N = 5) animals. E, Stereological counts of TH+ neurons in the SNc and VTA of a subset of animals (vehicle, N = 4; 6OHDA, N = 4). F–K, Summary excitability plots for excitatory neurons in L2/3 (green) and L5 (blue) of vehicle or 6OHDA-injected animals, performed in synaptic blockers (BLK: 20 μm picrotoxin, 20 μm DNQX, 50 μm AP5). Modified Cumming plots show raw data of individual neurons as swarm plots, with the mean ± SEM offset to the right. Further right of each group of raw data are the effect size (black circle), corresponding 95% CIs (black vertical bars), and the underlying bootstrap sampling distribution. F, Superimposed responses to hyperpolarizing and depolarizing current steps in individual L2/3 and L5 neurons in vehicle- or 6OHDA-injected animals. Scale bar: Top, 20 mV, 100 ms; bottom, 10 mV, 100 ms. G, Dynamic input resistance across hyperpolarizing current steps. H, Action potential threshold at rheobase. I, Action potential half-width at rheobase. J, Voltage dependence of Ih-mediated voltage sag elicited by hyperpolarizing current. K, Action potential frequency during suprathreshold current injections. Vehicle L2/3 neurons: N = 4, n = 12; vehicle L5 neurons: N = 5, n = 16; 6OHDA L2/3 neurons: N = 4, n = 14; 6OHDA L5 neurons: N = 4, n = 16. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. *p ≤ 0.05.
