Figure 1.
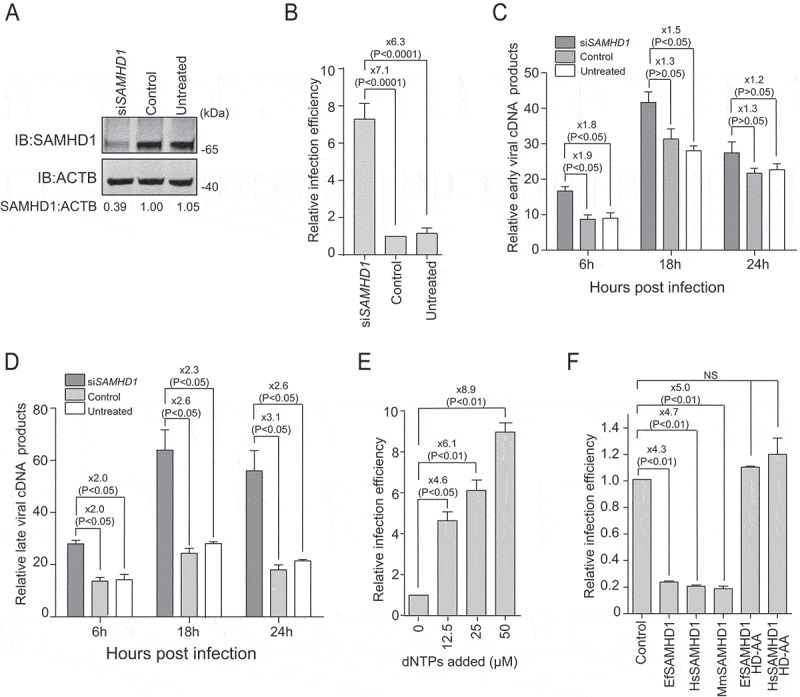
Equine SAMHD1 restricts EIAV infection. (A) Knockdown of the protein expression levels of EfSAMHD1. eMDMs were transfected with EfSAMHD1-specific siRNA or scrambled siRNA control. At 48 hpt, EfSAMHD1 protein levels were quantified by western blotting using ACTB as an internal control. The densities of EfSAMHD1 bands were analyzed with the Odyssey CLx Image Studio to calculate the values relative to that of ACTB. Results were normalized to control cells, which were set as 1. (B) Knockdown of EfSAMHD1 increases EIAV replication in equine macrophages. eMDMs transfected with the indicated siRNA were infected with EIAV luciferase reporter virus (RT = 10 ng). Cells were lysed, and luciferase activity in the cell lysates was measured at 48 hpi. Results were normalized to control cells. P > 0.05 was considered NS, P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (C and D) Knockdown of EfSAMHD1 increases viral reverse transcription products in eMDMs. EIAV luciferase reporter viruses were first treated with DNase and then used to infect eMDMs. Total DNA was collected, and the viral early (C) and late reverse transcripts (D) were quantified by real-time PCR using specific primers at 6, 12 and 18 hpi. ACTB was measured as an endogenous control. Data represent means and SD of three independent experiments. P > 0.05 was considered NS, P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (E) Adding dNTPs into eMDMs enhances the infection of EIAV in a dose-dependent manner. eMDMs were exposed to deoxynucleosides at different concentration, and then infected with EIAV luciferase reporter virus. Cells were lysed, and luciferase activity in the cell lysates was measured at 48 hpi. Results were normalized to control cells, which were set as 1. Data represent means and SD of three independent experiments. P > 0.05 was considered NS, P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (F) HD domain of EfSAMHD1 is essential for its antiviral activity. Stable U937 cell lines expressing wild-type SAMHD1 or SAMHD1 mutants were inoculated with EIAV luciferase reporter viruses. Cells were lysed, and luciferase activity in the cell lysates was measured at 48 hpi. Results were normalized to control cells, which were set as 1. Data represent means and SD of three independent experiments. P > 0.05 was considered NS, P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant
