Figure 7.
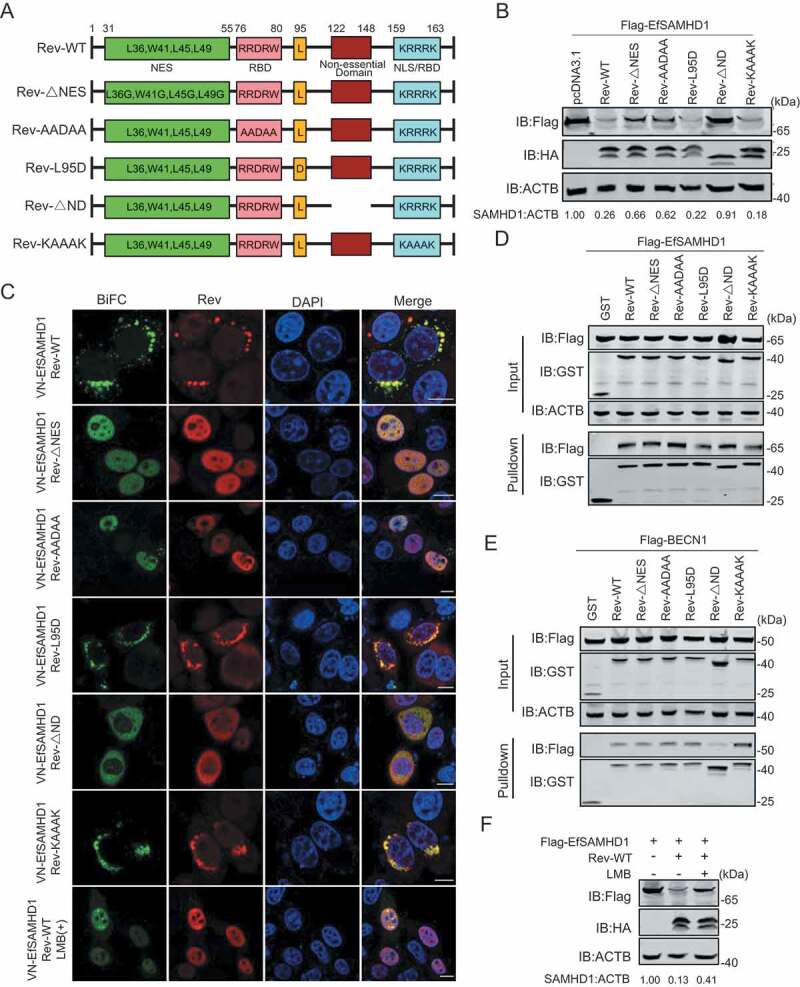
Identification of Rev domains crucial for equine SAMHD1 degradation. (A) Schematic diagram of wild-type EIAV Rev and structures of respective mutants. (B) Immunoblot analysis of EfSAMHD1 expression from the EfSAMHD1 and EIAV Rev mutant co-expression experiment. (C) Detection of BiFC green fluorescent signals from the EfSAMHD1 and EIAV Rev mutants co-expression experiment. HeLa cells were transfected with indicated plasmids. At 20 hpt, cells were either treated with LMB (5 nM) or not. After Incubation for 16 h, ectopic Rev proteins were stained with rabbit anti-HA antibodies, followed by Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated secondary antibodies. Colocalization of these fluorescent signals was visualized by confocal microscopy. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) GST affinity-isolation analysis of EfSAMHD1 and EIAV Rev mutants. (E) GST affinity-isolation analysis of EfBECN1 and EIAV Rev mutants. (F) LMB blocks Rev-induced EfSAMHD1 degradation. HEK293T cells were transfected with indicated plasmid. At 20 hpt, cells were treated with LMB (5 nM) or not. After Incubation for 16 h, the cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting. The densities of SAMHD1 bands were analyzed to calculate the values relative to that of ACTB. Results were normalized to control cells
