Figure 1.
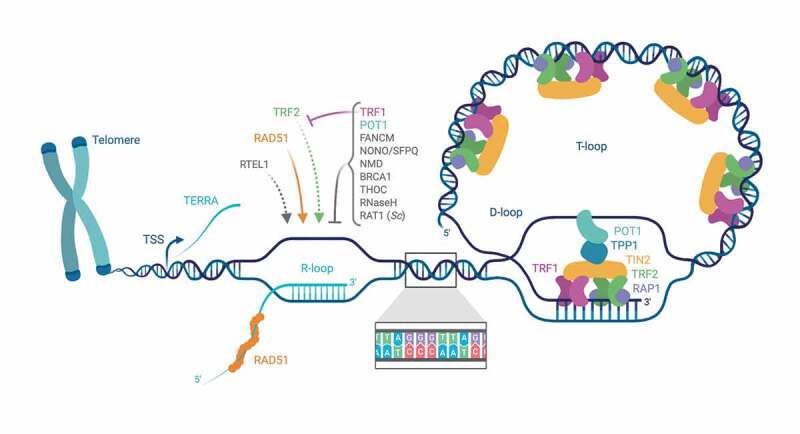
Cartoon of the nucleoprotein structure of chromosome ends; telomeric R-loops and its regulators. Among the numerous proteins associating with telomeres, the shelterin protein complex components are the most abundant, comprising the dsDNA-binding proteins TRF1 and TRF2, the ssDNA-binding protein POT1, TIN2, TPP1 and Rap1. Telomeres have a 3ʹ overhang, which can invade the dsDNA region, forming a D-loop which is termed T-loop. Telomeres are transcribed into TERRA. TERRA transcription starts at subtelomeric regions, extending toward chromosome ends. The vast majority of TERRA molecules is not polyadenylated and largely colocalizes with telomeres. TERRA binding to telomeres can occur through direct base-pairing with telomeric DNA, forming R-loop structures, leaving a displaced G-rich DNA strand. Factors which are suspected to regulate TERRA association with telomeres are indicated. TERRA association and R-loop formation at telomeres depend on the RAD51 DNA recombinase, which binds TERRA and catalyzes TERRA R-loop formation in vitro. Also, the helicase RTEL1 was proposed to stimulate TERRA association with chromosome ends via R-loops. The shelterin TRF2 can also bind TERRA and stimulate R-loop formation in vitro – a process counteracted in vivo by TRF1. Loss of POT1 was found to result in a striking accumulation of telomeric R-loops, suggesting a role in preventing the accumulation of such structures. Proteins involved in the NMD RNA surveillance pathway, including UPF1, UPF2 and SMG1, were also shown to prevent TERRA association with telomeres. The DNA recombination factor BRCA1 was as well shown to modulate TERRA binding to telomeres, preventing R-loop-associated telomeric DNA damage. The ATPase/translocase FANCM resolves RNA:DNA hybrids in vitro and counteracts telomeric R-loop accumulation in ALT cells. The THO multi-subunit complex is present at human and budding yeast telomeres, and was found to prevent R-loop accumulation and telomere shortening in budding yeast. RNase H enzymes – which remove RNA-DNA hybrids through the endonucleolytic cleavage of the engaged RNA moiety – were found to regulate TERRA R-loops, with a prominent role in ALT cells. In S. cerevisiae, Rat1 nuclease, as well as RNase H2, are preferentially recruited to long telomeres in S phase, preventing TERRA accumulation and formation of R-loops prone to pose an obstacle to telomeric replication. The Illustration was created with BioRender.com
