Figure 4.
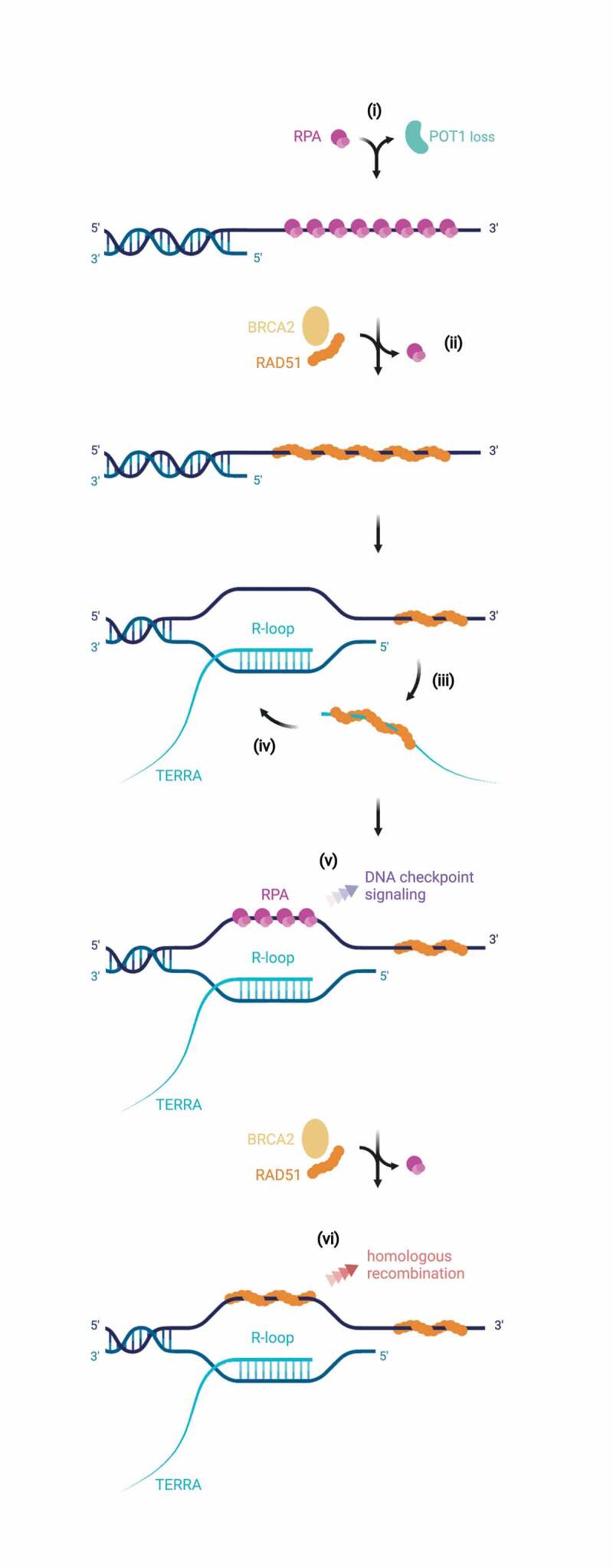
Possible R-loop- and RAD51-mediated telomere elongation mechanism upon loss of POT1. Loss of the ssDNA-binding shelterin POT1 at human telomeres leaves exposed the telomeric 3ʹ overhang – which can be bound by RPA (i). With assistance of BRCA2, RAD51 may displace and replace RPA (ii). This increased concentration of RAD51 at telomeres may facilitate binding of RAD51 to TERRA (iii), which subsequently can trigger strand invasion and R-loop formation (iv). Upon R-loop formation, the displaced single-stranded DNA strand can be bound by RPA – serving as a key platform for ATR activation (v). Assisted by BRCA2, RAD51 may then substitute RPA, mediating homologous recombination at the telomere (vi) eventually resulting in HDR-mediated telomere elongation (observed as a striking consequence of conditional deletion of POT1 in human cells). Illustration created with BioRender.com
