Figure 5.
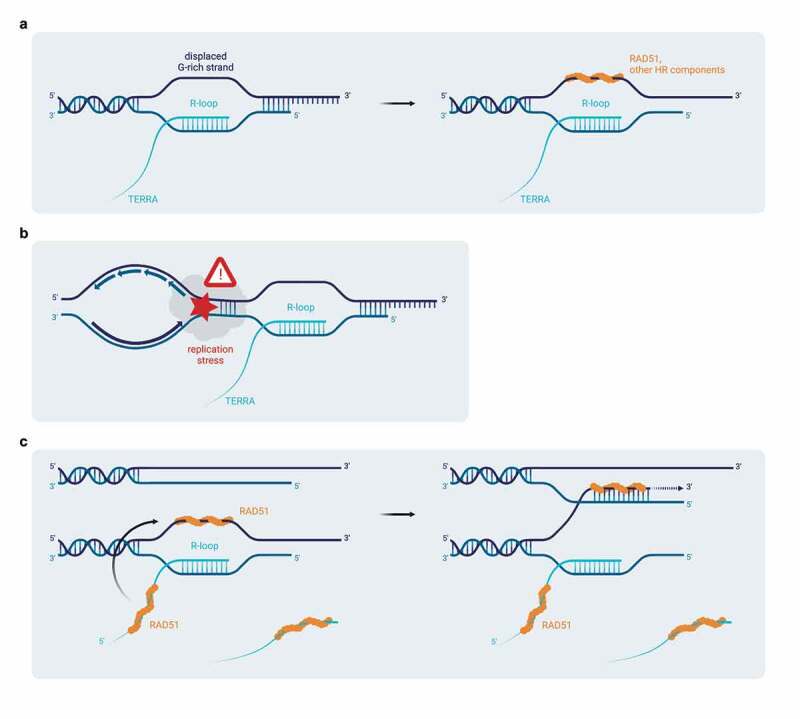
Possible mechanisms for TERRA R-loop-mediated stimulation of homologous recombination at telomeres. a) Upon R-loop formation, the displaced single-stranded DNA strand may facilitate the loading of the RAD51 recombinase and other recombination factors at telomeres. b) Telomeric R-loops pose a structural barrier that hinders progression of the replication machinery. Replication fork stalling may culminate in the formation of DNA double-strand breaks, which can then be repaired by homology-directed repair. c) RAD51-mediated stimulation of TERRA R-loops and association of RAD51 with the displaced DNA strand – exposed as a consequence of R-loop formation – may lead to local increased concentration of this recombinase and other recombination factors at telomeres, which in recombination-prone ALT cells may sustain telomeric homologous recombination and telomere elongation. Illustration created with BioRender.com
