Figure 2.
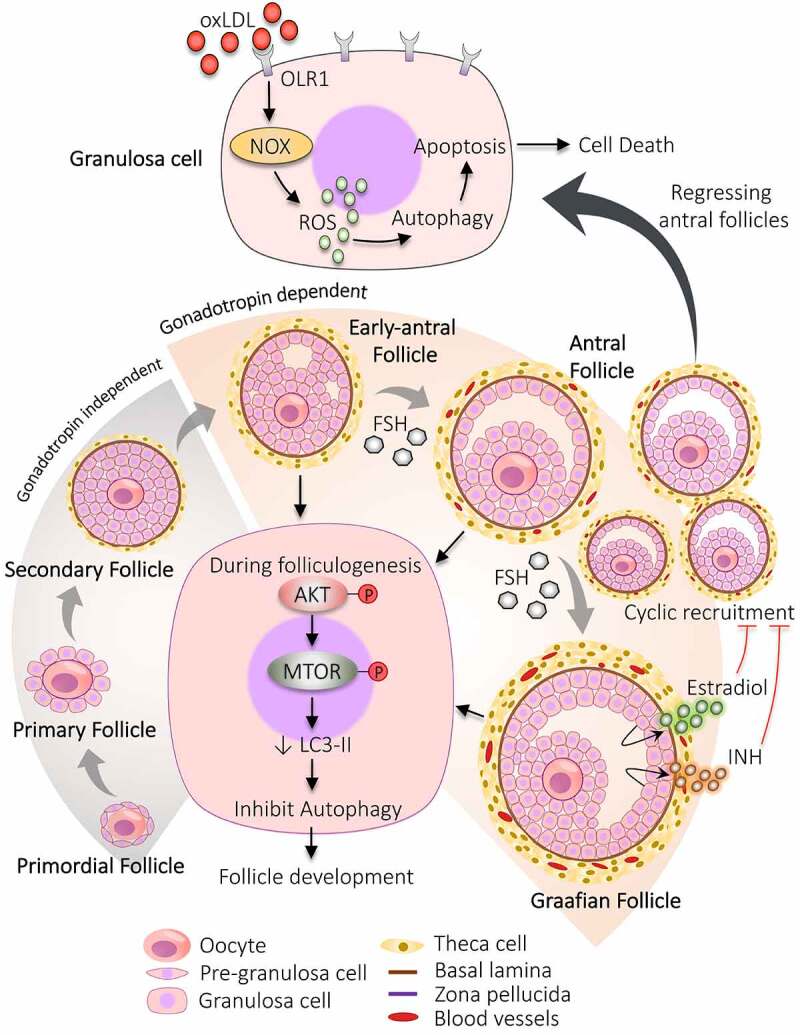
Participation of autophagy in the development of follicles. The developmental process begins with the formation of primordial follicles which is comprising of immature oocyte encircled by a single layer of pre-granulosa cells. The primary follicle is defined by granulosa cells with the appearance of zona pellucida. The proliferation of granulosa cells to multiple layers and the formation of theca cells layer results in the development of secondary follicle. Follicle with multiple small cavities is referred to as early antral follicles. A follicle with a single large cavity filled with antral fluid is called the antral follicle. Cyclic recruitment of antral follicles leads to the formation of a fully matured Graafian follicle. Estradiol and INH (inhibin) are secreted by the Graafian follicle, which stops the recruitment process. Activation of AKT and MTOR in granulosa cells prevents autophagy and favors follicular development. After the selection of dominant follicles, the remaining subordinate follicles are degenerated by autophagy-induced apoptosis. Increased expression of OLR1 receptor in granulosa cells of regressing follicles supports autophagy via inducing ROS production, resulting in granulosa cells death by apoptosis. NOX: NADPH oxidase
