Figure 7.
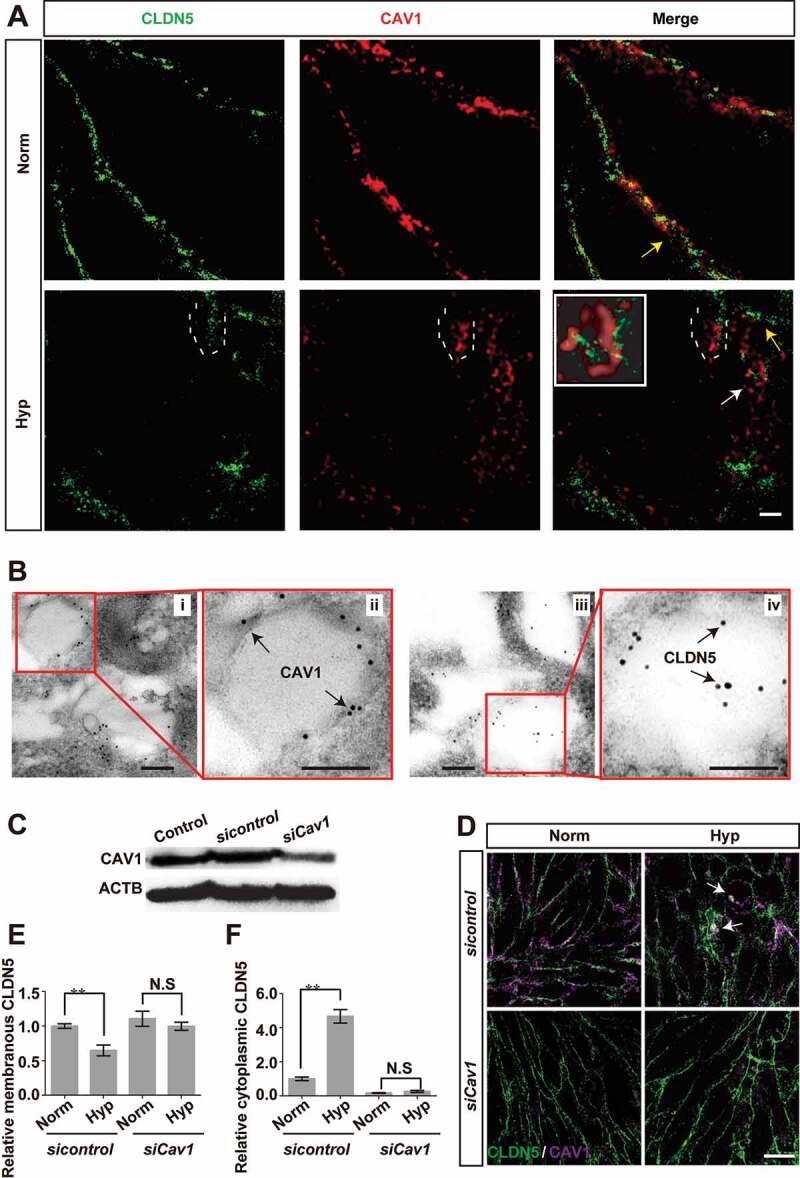
Caveolae-mediated endocytosis is involved in the redistribution of endothelial CLDN5 after hypoxia induction. (A) The localization of CLDN5 and CAV1 in bEnd.3 cells under CoCl2-induced hypoxia treatment was imaged by stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscope. White dotted lines-labeled region showed a surrounding of CLDN5 by CAV1 beneath the endothelial cell membrane (yellow arrows). Caveolae-liked vesicle packaging the aggregated CLDN5 (white arrow) was captured and the higher magnification image was shown in the white square. Scale bar: 1 μm. (B) CAV1 and CLDN5 in bEnd.3 cells under CoCl2-induced hypoxia treatment was imaged by immuno-electronmicroscope (IEM). Immunogold-labeled CAV1 was captured and found on the membrane of caveolae-liked vesicle while immunogold-labeled CLDN5 localized inside of the caveolae-liked vesicle. i and ii, normoxia control; iii and iv, hypoxia-treated group. ii and iv are high magnification scans of the red line-marked regions in i and iii respectively. Scale bars: 100 nm. (C-F) After knock-down of Cav1, the redistribution of membranous CLDN5 into the cytosol of bEnd.3 cells (white arrows in D) was suppressed under CoCl2-induced hypoxic conditions. The integrated optical density (IOD) of membranous or cytosolic CLDN5 was quantified. CoCl2: 200 μmol/L, treated for 12 h; Norm: normoxia; Hyp: hypoxia. sicontrol: monolayer of bEnd.3 was transiently transfected with scrambled negative control siRNA. siCav1: monolayer of bEnd.3 was transiently transfected with Cav1 siRNA. n = 3 images for each experiment. Data were presented as mean ± SEM. P value indicates one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. **, P < 0.01. N.S: no significance. Scale bar: 10 μm
