Figure 4.
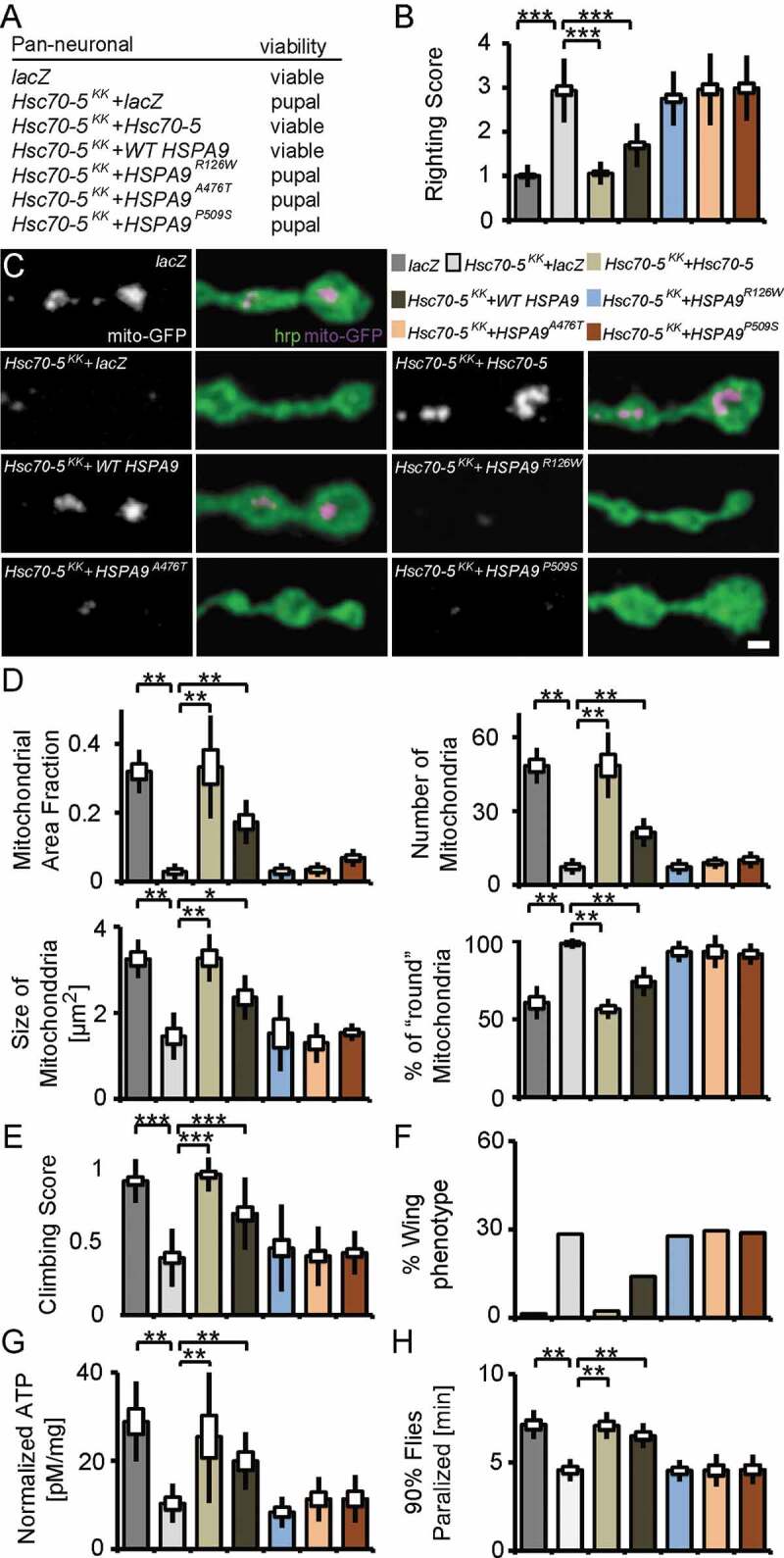
Drosophila Hsc70-5 and human WT HSPA9 but not disease variants rescued Hsc70-5 knockdown phenotypes. (A) Hsc70-5 knockdown in combination with lacZ overexpression to control Gal4 dilution at 25°C caused pupal lethality. Overexpression of Drosophila Hsc70-5 and human WT HSPA9 in the Hsc70-5KK100233 background unlike HSPA9R126W, HSPA9A476T and HSPA9P509S variants rescued pupal lethality. (B) Average larval righting reflex at L3 stage with overexpression of Hsc70-5, WT HSPA9, HSPA9R126W, HSPA9A476T and HSPA9P509S in the elav>Hsc70-5KK100233 background. (C) Confocal images of larval NMJ labeled with hrp (green) and mito-GFP (magenta), and (D) quantification of mitochondrial parameters. Scale bar: 2 μm. (E) Climbing ability of 4-d-old flies, (F) Percentage of flies with defective wing phenotype, and (G) ATP levels in fly heads after expressing Hsc70-5, WT HSPA9, HSPA9R126W, HSPA9A476T and HSPA9P509S in the elav>Hsc70-5KK100233 background. (H) Hsc70-5 knockdown accelerated heat-shock induced paralysis in flies at 39.5°C. The co-overexpression of Hsc70-5 and WT HSPA9 unlike HSPA9R126W, HSPA9A476T and HSPA9P509S rescued this defect. The standard error of mean and standard deviation are shown as a box and a black line. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001
