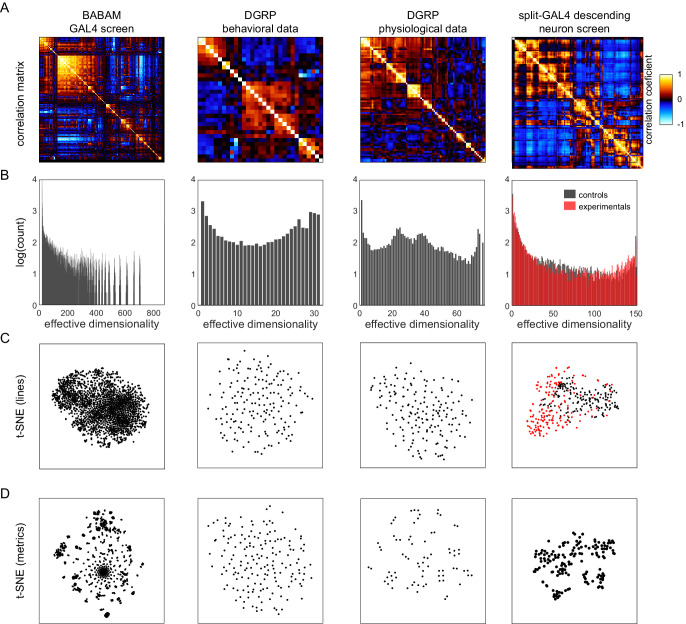
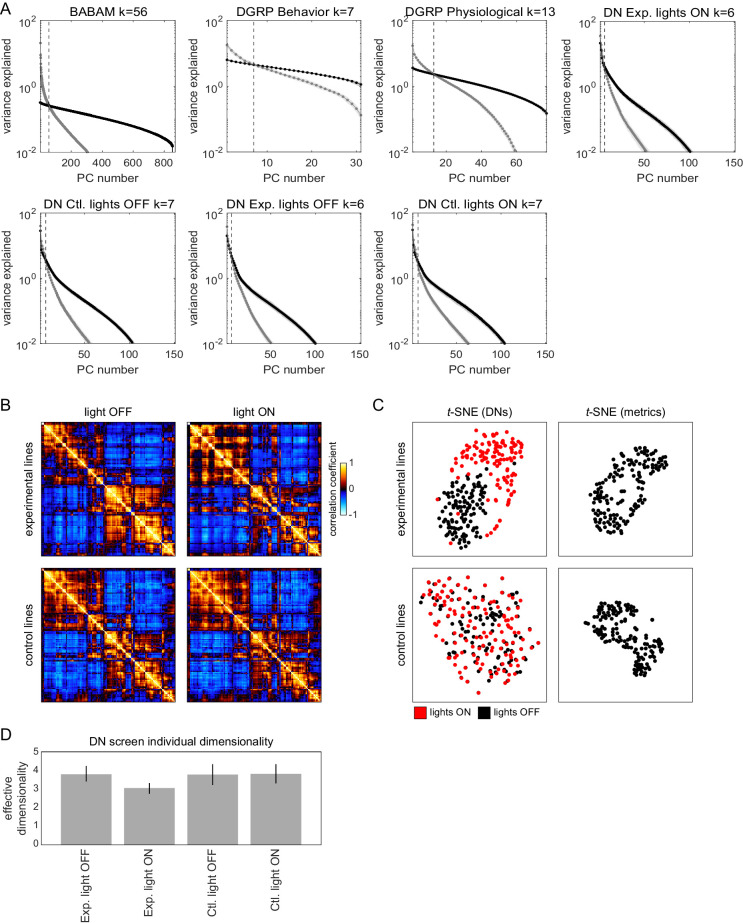
Figure 5. Analysis of Drosophila behavioral covariation in other non-isogenic populations.
(A) Correlation matrices of previously published data sets. Rows correspond to analyses performed on each data set. From left to right, the data sets (columns) are as follows: line averages of supervised behavioral classifications following thermogenetic inactivation in the fly olympiad screen (Robie et al., 2017), line averages of behavioral phenotypic data from wild-type inbred lines in the Drosophila Genomic Reference Panel (DGRP) database, line averages of physiological phenotypic data from the DGRP database, line averages of the fold change in unsupervised behavioral classifications following optogenetic activation of descending neurons (Cande et al., 2018). (B) Connected components spectra for each correlation matrix (see Materials and methods). Color in the rightmost plots (B–D) indicates either control (Gal4 driver only) or experimental animals (Gal4 × dTrapA1). (C) Points corresponding to lines nonlinearly embedded using t-SNE from the D-dimensional raw measure space to two dimensions (from left to right, d = 871, 31, 77, 151). (D) Points corresponding to lines nonlinearly embedded using t-SNE from the n-dimensional raw measure space to two dimensions (from left to right, n = 2083, 169, 169, 176).