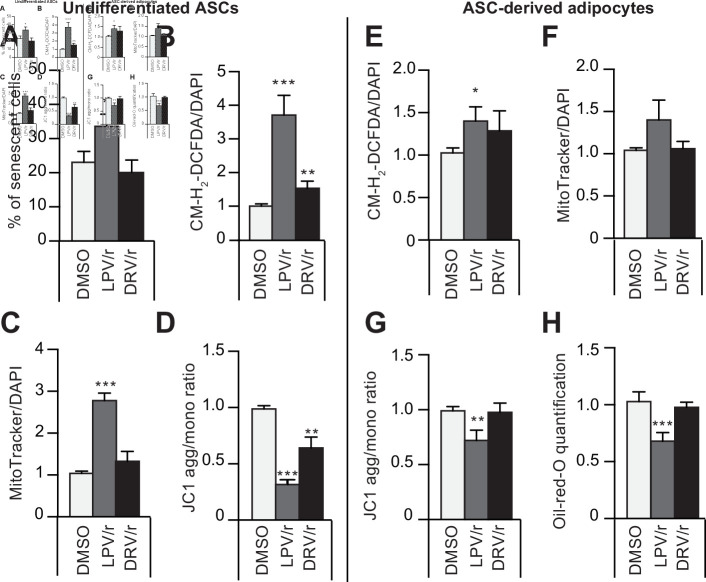
Figure 5. The protease inhibitors (PIs) lopinavir/r and darunavir/r induce, at different extents, in young-donor adipose-derived stromal cells (ASCs) at early passage senescence, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction leading or not to altered ASC-derived adipocytes.
ASCs were treated during 30 days with DMSO or PIs: lopinavir (LPV) or darunavir (DRV) associated with a low dose of ritonavir (LPV/r or DRV/r) (A–D). The ASCs were then differentiated into adipocytes for 14 days in the absence of PIs (E–H). (A) ASCs’ senescence was evaluated in terms of senescence-associated (SA)-β-galactosidase activity and expressed as the proportion (in %) of SA-β-galactosidase-positive cells at pH 6. (B) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (normalized against 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride [DAPI]) was assessed by the oxidation of CM-H2DCFDA and expressed as a ratio relative to DMSO. (C) Mitochondrial mass (normalized against DAPI) was evaluated with Mitotracker Red-Probe and expressed as a ratio relative to DMSO. (D) The cationic dye JC1 was used to evaluate the mitochondrial membrane potential. In ASC-derived adipocytes, 14 days post-induction, (E) ROS production (F) mitochondrial mass, and (G) mitochondrial membrane potential normalized to DAPI were evaluated. (H) Cells were stained with Oil-Red-O to visualize lipid droplets. Results are quoted as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. DMSO. All experiments were performed in triplicate with ASCs isolated from three different donors in each group.