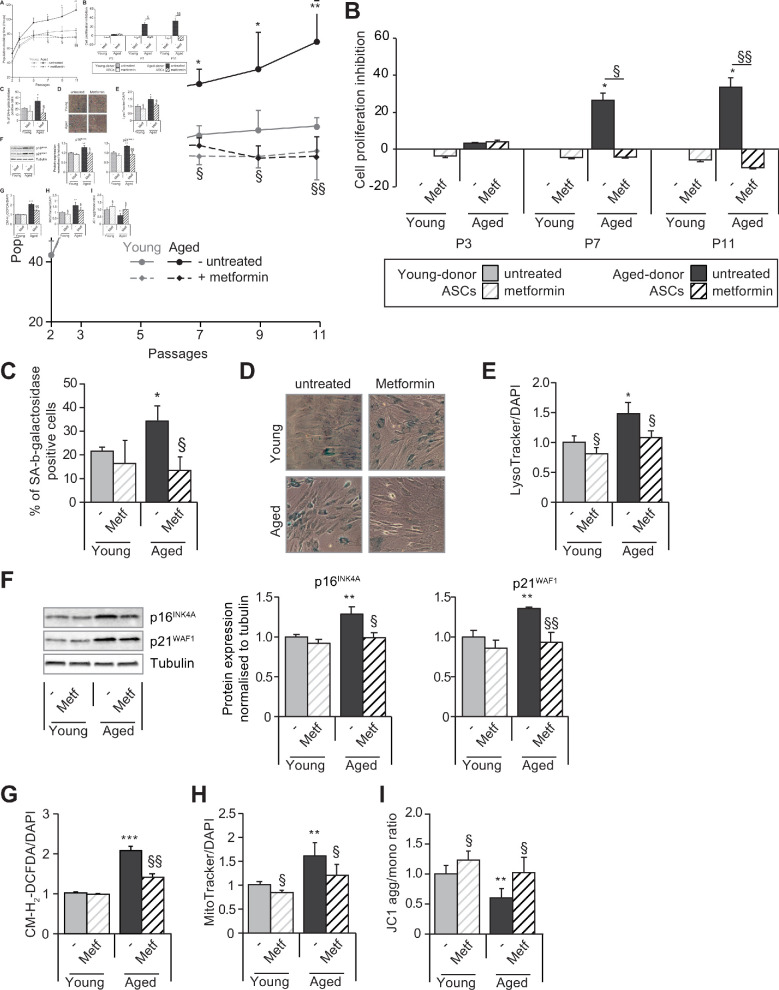
Figure 6. Metformin partially prevents the senescence and associated dysfunctions in adipose-derived stromal cells (ASCs) obtained from aged donors but not in those obtained from young donors.
Metformin (25 µmol/L) was added to the culture medium of aged-donor and young-donor ASCs from P3 onward (young-donor ASC: gray dots and bars in the absence of metformin, gray dotted lines or gray striped bars in the presence of metformin; aged-donor: black circles and bars in the absence of metformin, black dotted lines and striped bars in the presence of metformin). Mean population doubling times (PDT) were determined at the indicated passages in aged-donor and young-donor ASCs treated (or not) with metformin at the same passage. (B) The % inhibition of cell proliferation was calculated for aged-donor ASCs and young-donor ASCs treated by metformin by determining the increase in total cell number that occurred after 7 days, compared to young-donor ASCs. (C) Senescence was evaluated in terms of senescence-associated (SA)-β-galactosidase activity and expressed as the proportion (in %) of SA-β-galactosidase-positive cells at pH 6 in metformin-treated ASCs vs. non-treated ASCs at P11. (D) Representative micrographs of SA-β-galactosidase positive cells. (E) Lysosomal accumulation (normalized against 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride [DAPI]) was assessed with the Lysotracker fluorescence probe in metformin-treated ASCs vs. non-treated ASCs at P11. (F) Whole-cell lysates of aged-donor and young-donor ASCs treated (or not) with metformin were analyzed at P11 by immunoblotting. Representative immunoblots of the cell cycle arrest markers p16INK4A and p21WAF1 and of tubulin (the loading control) for two donors in each group are shown. Quantitation of western blots, normalized against the values for non-treated young-donor ASCs at P11. (G) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, (H) mitochondrial mass (both normalized against DAPI) and (I) mitochondrial membrane potential were assessed as described in Figure 1 in metformin-treated ASCs vs. non-treated ASCs at P11. The results correspond to the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for aged-donor vs. young-donor ASCs, §p < 0.05, §§p < 0.01 metformin-treated vs. non-treated ASCs. All experiments were performed in duplicate or triplicate in ASCs isolated from three different donors in each group.