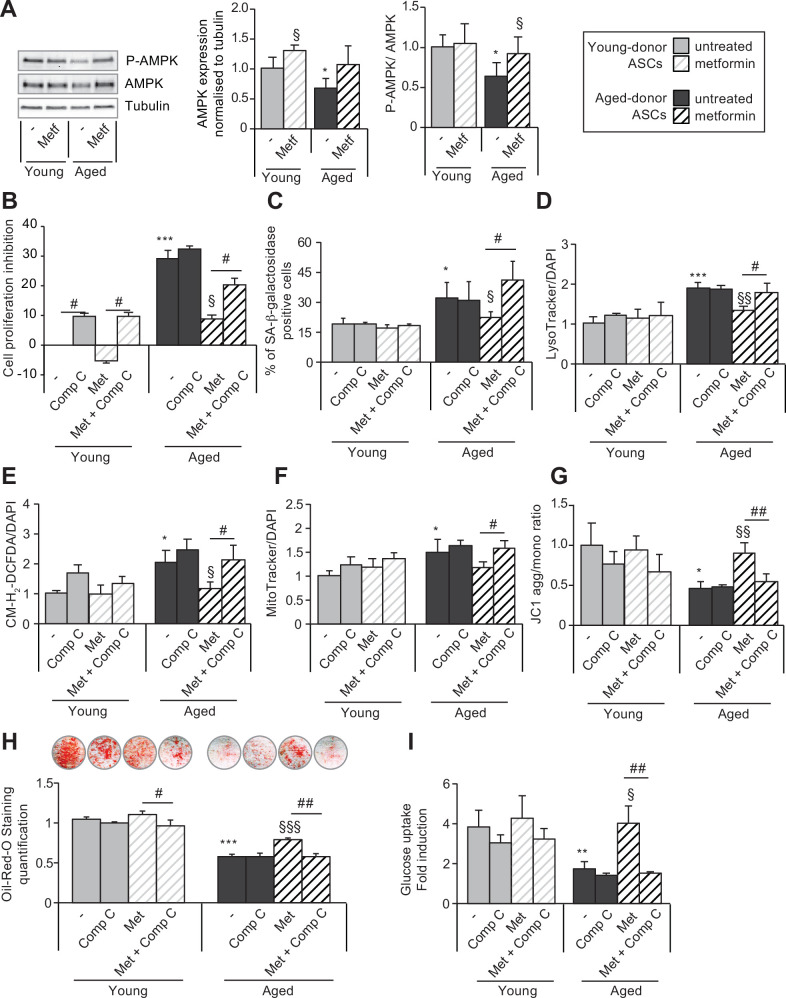
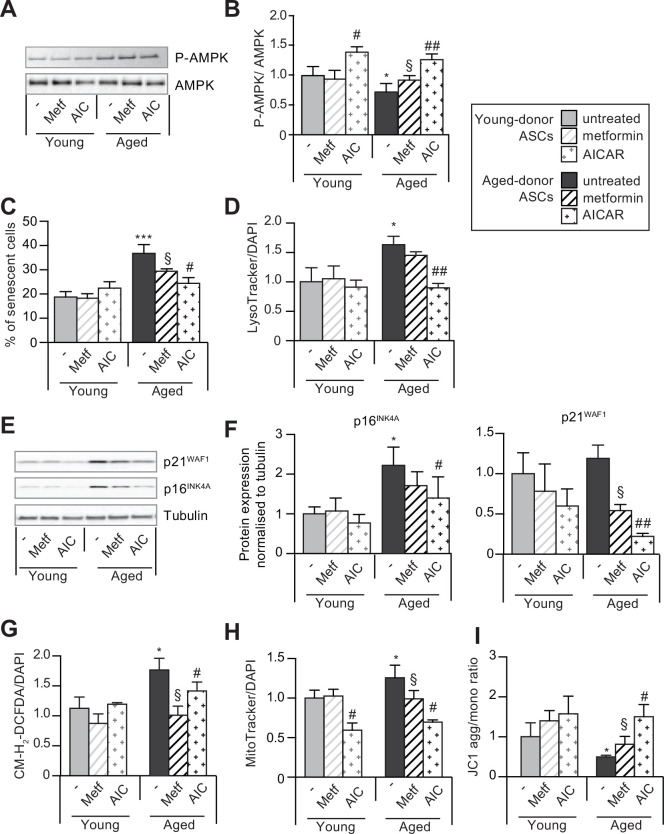
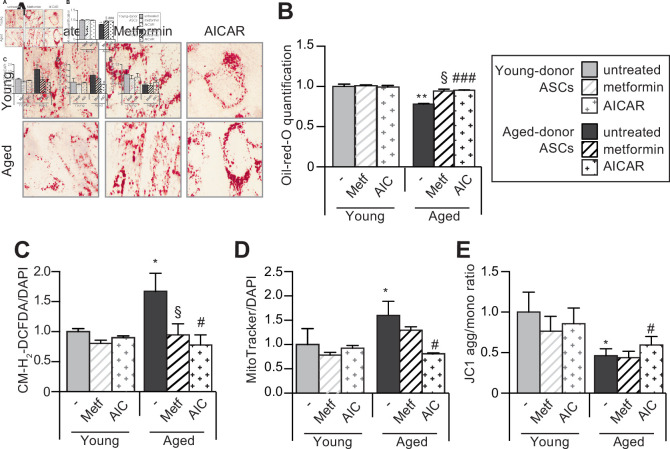
Figure 8. The beneficial effects of metformin on aged-donor adipose-derived stromal cell (ASC) senescence is mediated by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation.
Metformin was added to the culture medium of aged-donor and young-donor ASCs from P3 onward. To evaluate the role of AMPK activation, compound C was added at P11. After 7 days of treatment, the experiments on ASCs were carried out (young-donor ASC: gray bars in the absence of metformin or in the presence of compound C, gray striped bars in the presence of metformin or metformin and compound C; aged-donor: black bars in the absence of metformin or in the presence of compound C, black striped bars in the presence of metformin or metformin and compound C). (A) Whole-cell lysates of aged-donor and young-donor ASCs treated (or not) with metformin and compound C at P11 were analyzed by immunoblotting. Representative immunoblots of AMPK, phospho-AMPK, and tubulin (the loading control) and a graph quantifying AMPK (normalized against tubulin) and the pAMPK/AMPK ratio are shown. (B) The % inhibition of cell proliferation was calculated for aged-donor ASCs and young-donor ASCs treated or not with metformin or compound C, by determining the increase in total cell number that occurred after 7 days, compared to young-donor ASCs. (C) Senescence was evaluated in terms of senescence-associated (SA)-β-galactosidase activity and was expressed as described in Figure 1. (D) Lysosomal accumulation (normalized against 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride [DAPI]) was assessed with the Lysotracker fluorescence probe. (E) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, (F) mitochondrial mass (both normalized against DAPI), and (G) mitochondrial membrane potential were assessed as described in Figure 1. (H) The ASCs were then differentiated into adipocytes on P11 in the absence of metformin and compound C. Cells were stained with Oil-Red-O to visualize lipid droplets 14 days post-induction. Quantification of Oil-Red-O staining and representative scans of wells are shown. (I) Insulin sensitivity was evaluated at P11 in adipocytes differentiated from non-treated young-donor and aged-donor ASCs treated (or not) with metformin and/or compound C, by measuring the glucose uptake in response to insulin and calculating the insulin fold induction, as described in the Materials and methods section. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 for aged-donor vs. young-donor ASCs, §p < 0.05, §§p < 0.01 for metformin-treated ASCs vs. non-treated ASCs. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 for compound C and metformin-treated ASCs vs. metformin-treated ASCs. All experiments were performed in duplicate or triplicate on ASCs isolated from at three different donors in each group.