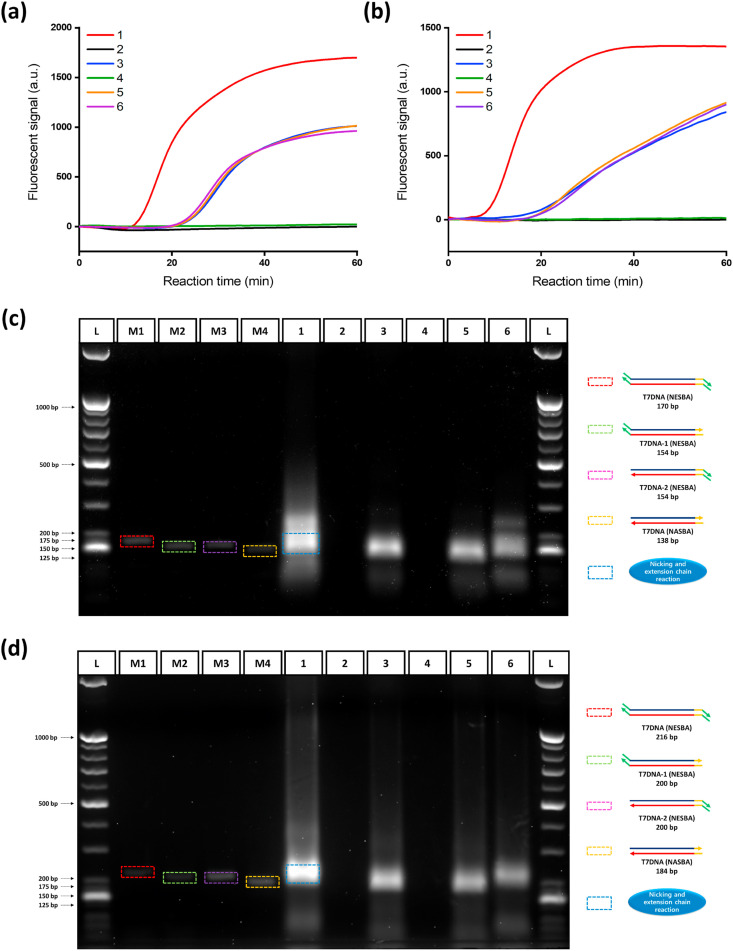
Fig. 2.
Feasibility test of the NESBA for E and N genes of SARS-CoV-2 gRNA. Time-dependent fluorescent signals produced from gene-specific MBs during the NESBA reaction for (a) E and (b) N genes. Agarose gel electrophoresis image of the products obtained after 45 min NESBA reaction for (c) E and (d) N genes (1: Target gRNA + E(I) or N(I)-NESBA primer set + NASBA enzyme cocktail + NE, 2: E(I) or N(I)-NESBA primer set + NASBA enzyme cocktail + NE, 3: Target gRNA + E or N-NASBA primer set + NASBA enzyme cocktail, 4: E or N-NASBA primer set + NASBA enzyme cocktail, 5: Target gRNA + E or N-NASBA primer set + NASBA enzyme cocktail + NE, and 6: Target gRNA + E(I) or N(I)-NESBA primer set + NASBA enzyme cocktail). The final concentration of SARS-CoV-2 gRNA is 5 × 105 copies/μL. M1-M4 are markers for band analysis (L: 25/100 bp mixed DNA ladder, M1: T7DNA (NESBA), M2: T7DNA-1 (NESBA), M3: T7DNA-2 (NESBA), M4: T7DNA (NASBA). We obtained the representative lines in (a) and (b) from the triplicate experiments and the reproducibility of the experiments were confirmed by the CV values for Tt in Table S5, which were all smaller than 5%. Tt is the time when the fluorescent signal reaches the threshold (100 a.u.) and CV is calculated as (Standard deviation of Tt)/(Mean of Tt) × 100. The final concentrations of markers used for M1-M4 are 100 nM.