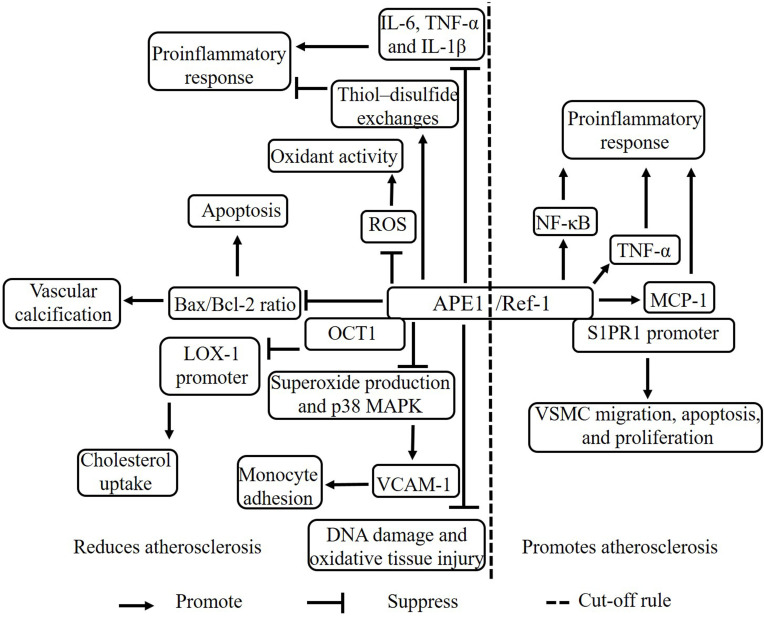
Figure 1.
The mechanism of APE1/Ref-1 in atherosclerosis. APE1/Ref-1 has both proatherogenic and antiatherogenic effects. APE1/Ref-1 suppresses atherosclerosis via multiple mechanisms. APE1/Ref-1 reduces the proinflammatory response by increasing thiol–disulfide exchanges and suppressing the expression of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β. APE1/Ref-1 reduces oxidant activity by suppressing ROS levels and decreases vascular calcification and apoptosis by suppressing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. APE1/Ref-1 reduces cholesterol uptake by binding OCT1 to inhibit activation of the LOX-1 promoter. APE1/Ref-1 decreases monocyte adhesion by suppressing superoxide production and p38 MAPK expression to restrain VCAM-1. APE1/Ref-1 reduces DNA damage and oxidative tissue injury. APE1/Ref-1 promotes atherosclerosis via multiple mechanisms. APE1/Ref-1 increases the proinflammatory response by increasing NK-κB pathway signaling and TNF-α and MCP-1 expression. APE1/Ref-1 promotes VSMC migration, apoptosis, and proliferation by binding the S1PR1 promoter.