FIGURE 1.
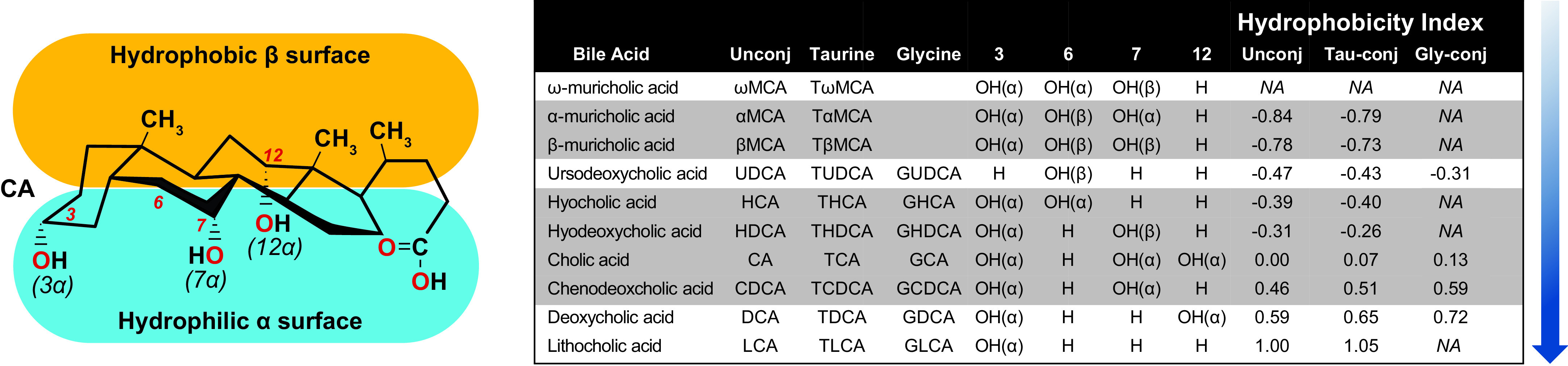
Bile acid (BA) hydrophobicity is determined by the number and position of hydroxyl and sulfate groups to the sterol ring as well whether the BA is conjugated to an amino acid, which in mice is predominantly taurine and in humans is mostly glycine. Hydroxylation at carbons 3, 6, 7, and 12 on the sterol core of primary (highlighted gray) and secondary (white) BAs increases the BA hydrophobicity index (blue shaded arrow). Adapted from Heuman et al. (7).
