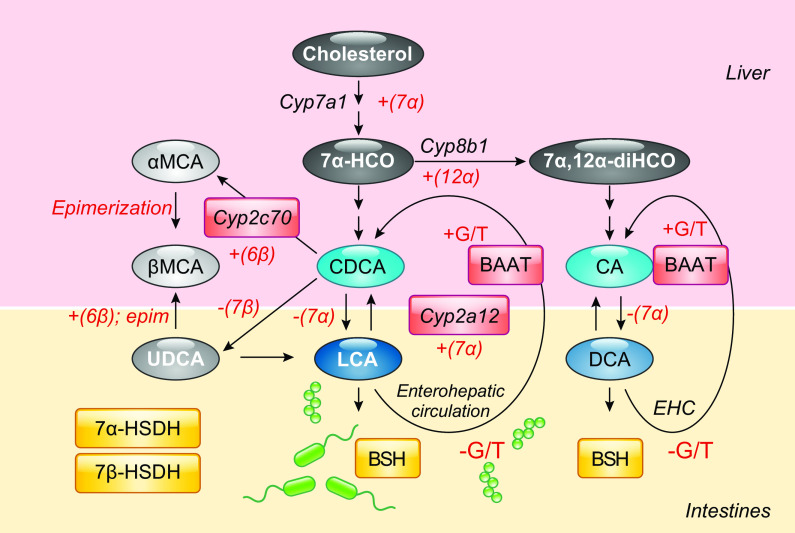
FIGURE 2.
Bile acid (BA) biosynthesis and metabolism in the liver and intestine. The primary BAs, chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and cholic acid (CA) are synthesized from cholesterol and other precursors via Cyp7a1 in the liver yielding the precursors 7α-hydroxycholesterol (7α -HCO) and (7,12-dihydroxycholesterol (7α,12α-diHCO), respectively, the latter generated via the 12α-hydroxylase activity of Cyp8b1. In mice, Cyp2c70 6-hydroxylates CDCA yielding α-muricholic acid (αMCA), which is further epimerized into βMCA and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) via the same enzyme. CA and CDCA are primary BAs in humans while CA, CDCA, MCAs, and UDCA, are primary BAs in mice. After conjugation with glycine (G) or taurine (T) via hepatic BA amino transferase (BAAT), these BAs are secreted into bile which is then released into the intestines. Bacterial 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7α-HSDH) generates deoxycholic acid (DCA), and lithocholic acid (LCA) and 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7β-HSDH) render UDCA. Hepatic Cyp2a12 rehydroxylates DCA and LCA into CA and CDCA, respectively. In humans, CA, CDCA, and DCA are conjugated derivatives are predominant. In mice, CA, αMCA, and βMCA and conjugated derivates are predominant. Cyp2c70-/- mice have increased CDCA and are void of MCAs. Cyp2a12-/- mice have increased DCA, CDCA, and LCA. Cyp2c70-/- and Cyp2a12-/- [double knockout (DKO)] mice have increased DCA, CDCA, and LCA.