Figure 1. Clock components in cancer cells affect TME biology.
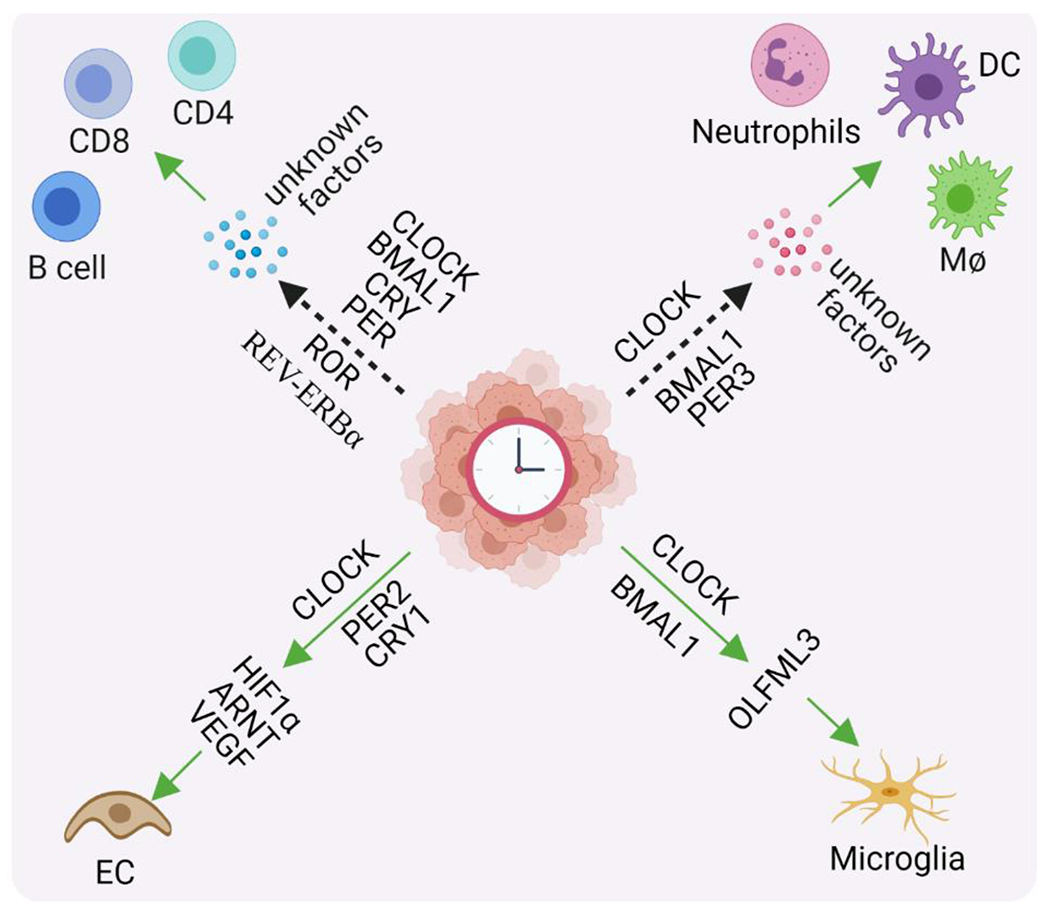
Clock components, including circadian clock and clock genes/proteins (e.g., CLOCK, ARNTL/BMAL1, PER, CRY, RORs, and REV-ERBα) in cancer cells or cancer stem cells regulate the expression and secretion of soluble factors (e.g., HIF1α, ARNT, VEGF, OLFML3, and other unidentified factors). Consequently, these secreted factors modulate TME biology, including endothelial cell (EC) biology (e.g., promoting angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic therapy resistance), infiltration of myeloid cells [e.g., macrophages (MΦ), microglia, neutrophils, and dendritic cells (DC)], as well as infiltration and activation/suppression of lymphocytes (e.g., CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, and B cells). The dash arrows indicate that clock components are correlated with the infiltration of immune cells. Abbreviations: ARNT, aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; BMAL1, brain and muscle ARNT-like protein-1; CLOCK, circadian locomotor output cycles kaput; CRY, cryptochrome; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; OLFML3, olfactomedin-like 3; PER, period; ROR, retinoic acid receptor—related orphan receptor; and VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
