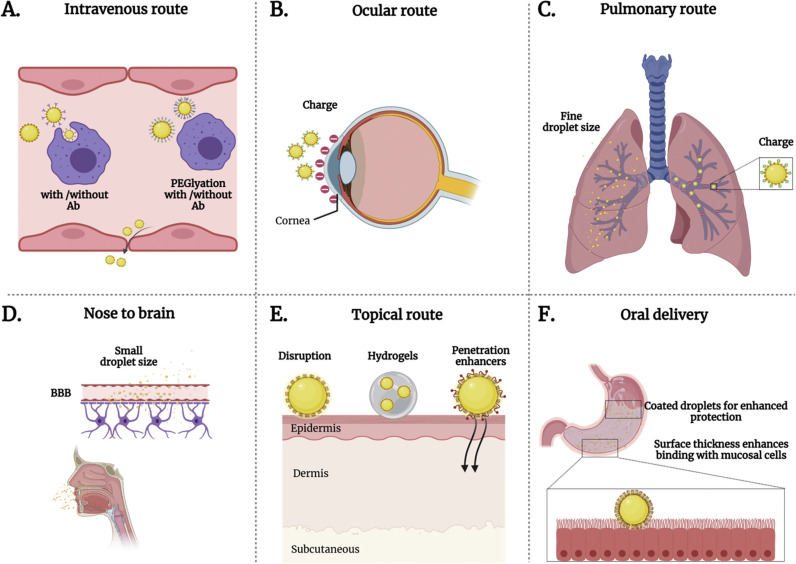
Fig. 5.
Administration routes with highlighted strategies using NEs surface designs to overcome biological barriers. A. Intravenously administered NEs functionalized with PEG to escape from macrophages and achieve therapeutic delivery. B. Cationic NEs targeting cornea for potential intracellular drug delivery. C. Pulmonary and nasal drug delivery through cationic NEs with fine droplet size. D. Nose to brain delivery of therapeutic NEs crossing the blood-brain barrier with small droplet size and hydrophobic interactions. E. Dermal drug delivery of NEs through surface disruption (surface tension, thermodynamic activity), hydrogels, and penetration enhancers. F. Surfactant-stabilized NEs orally administered to overcome harsh gastric environment, e.g., gastric juices, and increased surface thickness for enhanced adhesion with targeted tissues.