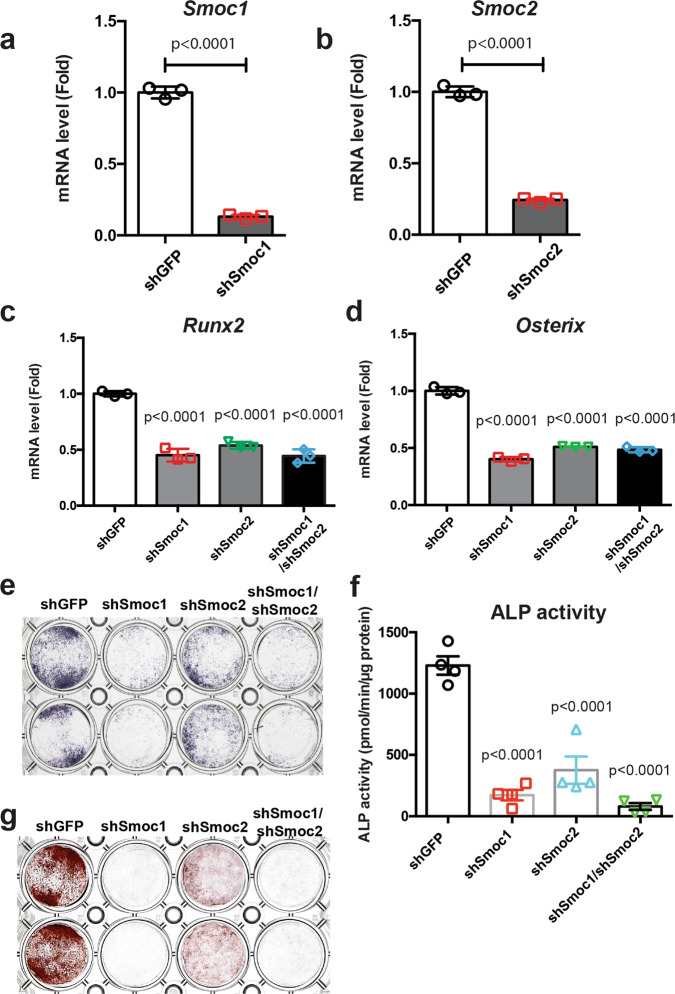
Fig. 3. Roles of Smoc1 and Smoc2 in osteoblast differentiation.
a–d Primary osteoblasts isolated from mouse calvariae were infected with shGFP, shSmoc1, shSmoc2, or both shSmoc1 and shSmoc2 retroviruses. At 72 h after infection, the culture medium was replaced with a new medium and the cells were infected with Bmp2 adenovirus for 6 h, followed by incubation in a differentiation medium containing 50 μg/mL ascorbic acid and 5 mM sodium β-glycerophosphate for 5 days. Total RNA was extracted from the cells and expressions of Smoc1 (a), Smoc2 (b), Runx2 (c), and Osterix (d) mRNAs were determined by RT-qPCR. Values are the mean ± SE (n = 3, biologically independent samples). e–g Primary osteoblasts isolated from mouse calvariae were infected with shGFP, shSmoc1, shSmoc2, or both shSmoc1 and shSmoc2 retroviruses. The cells were infected with Bmp2 adenovirus and incubated in the presence of 50 μg/mL ascorbic acid and 5 mM sodium β-glycerophosphate. After incubation for 3 or 5 days, the cells were evaluated by alkaline phosphatase staining (n = 3, independent experiments) (e), alkaline phosphatase activity (n = 4, biologically independent samples) (f), and alizarin red staining (g) (n = 3, independent experiments).