Figure 4: Impaired cell-to-cell adhesion in aged keratinocytes monolayers.
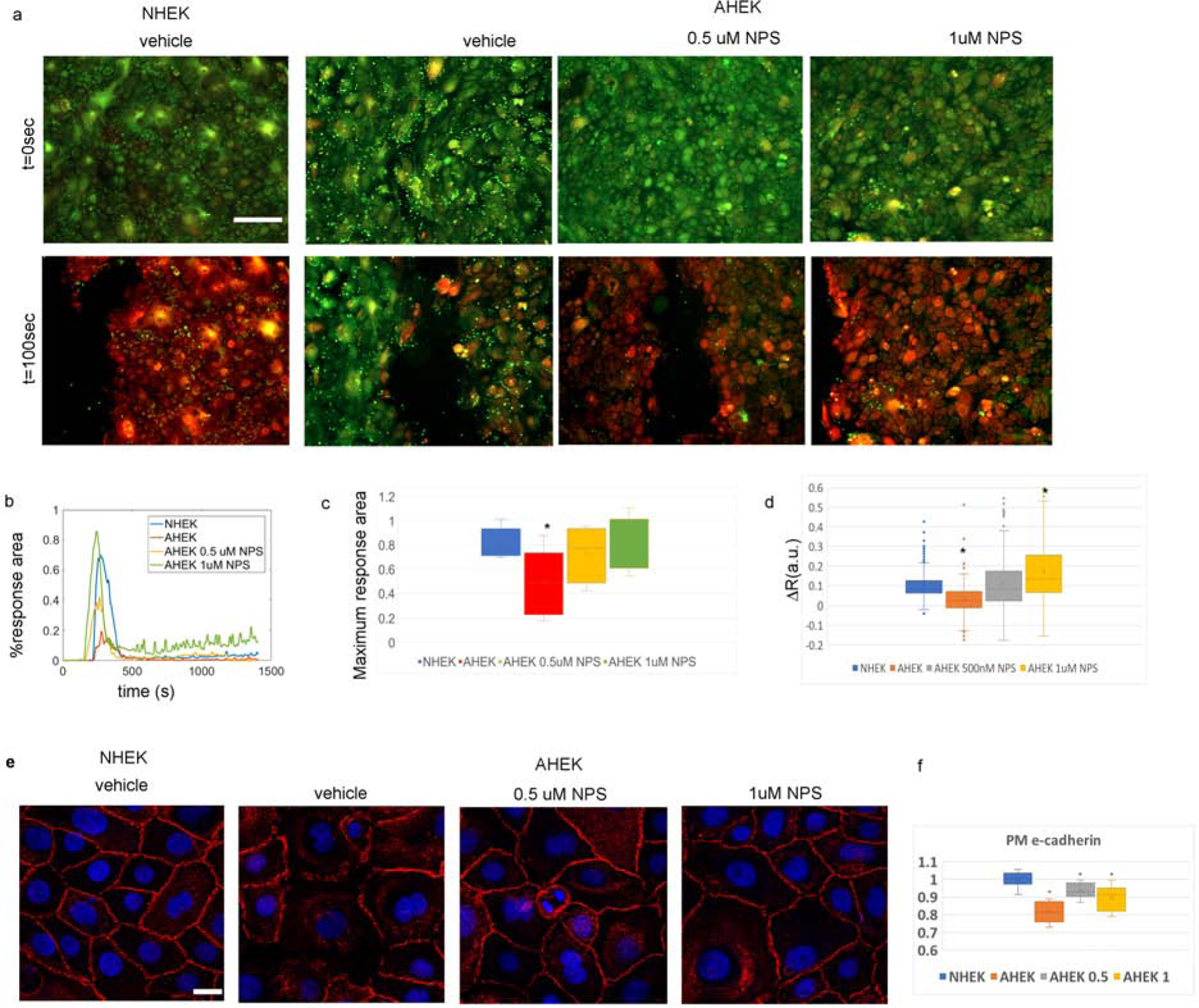
(a) Brightfield time-lapse images of scratch assay of second passage keratinocytes monolayers from neonatal (top row) and aged (bottom row) donors in high calcium. Yellow lines highlight the gap area at different timepoints, while red lines highlight gaps occurring in the AHEK monolayers during sheet migration. Inset shows gaps in aged epidermal keratinocytes sheet. (b) Mean percentage gap closure as a function of time. AHEK blue bars, NHEK orange bars. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. N=4–8 wells from two experiments on cells from 3–4 donors per condition. (c-d) E-cadherin staining (red) of NHEK (c) and AHEK (d) monolayers 6 hours after scratching. Nuclear DAPI counterstain (blue). Insets show higher detail of e-cadherin staining. White arrows in d show gaps in cell-to-cell adhesion.
