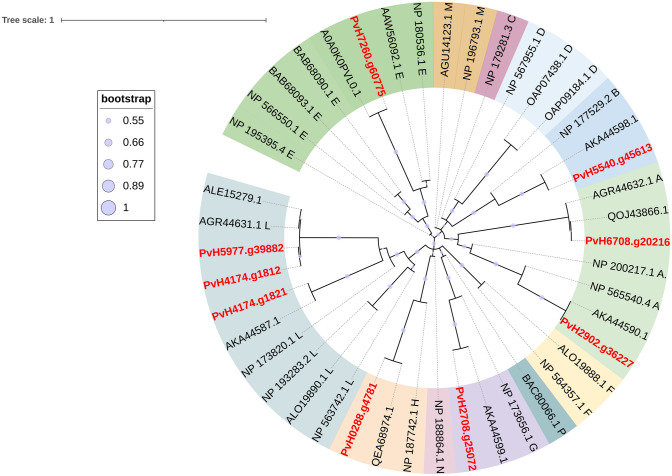
Fig. 8.
Phylogenic analysis of UGTs candidates of Vietnamese ginseng and various species. UGTs of Panax Vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. were highlighted in red (PvH5977.g39882, PvH6708.g20216, PvH2708.g25072, PvH5540.g45613, PvH2902.g36227, PvH0288.g4781, PvH4174.g1821, PvH4174.g1812, PvH7260.g60775). Genbank accession numbers of UGTs from different species including Panax quinquefolius (ALE15279.1), Panax ginseng (AKA44599.1, AKA44598.1, AKA44590.1, QEA68974.1, AKA44587.1, A0A0K0PVL0.1, AGR44632.1, AGR44631.1), Panax notoginseng (QOJ43866.1), Arabidopsis thaliana (OAP09184.1, OAP07438.1, NP_173656.1, NP_173820.1, NP_177529.2, NP_179281.3, NP_180536.1, NP_187742.1, NP_188864.1, NP_193283.2, NP_195395.4, NP_196793.1, NP_200217.1, NP_563742.1, NP_564357.1, NP_565540.4, NP_566550.1, NP_567955.1), Cicer arietinum (AGU14123.1), Camellia sinensis (ALO19890.1, ALO19888.1), Medicago truncatula (AAW56092.1), and Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (BAB68090.1, BAB68093.1, BAC80066.1). The letters of A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, L, M, N, and P are groups of UTGs