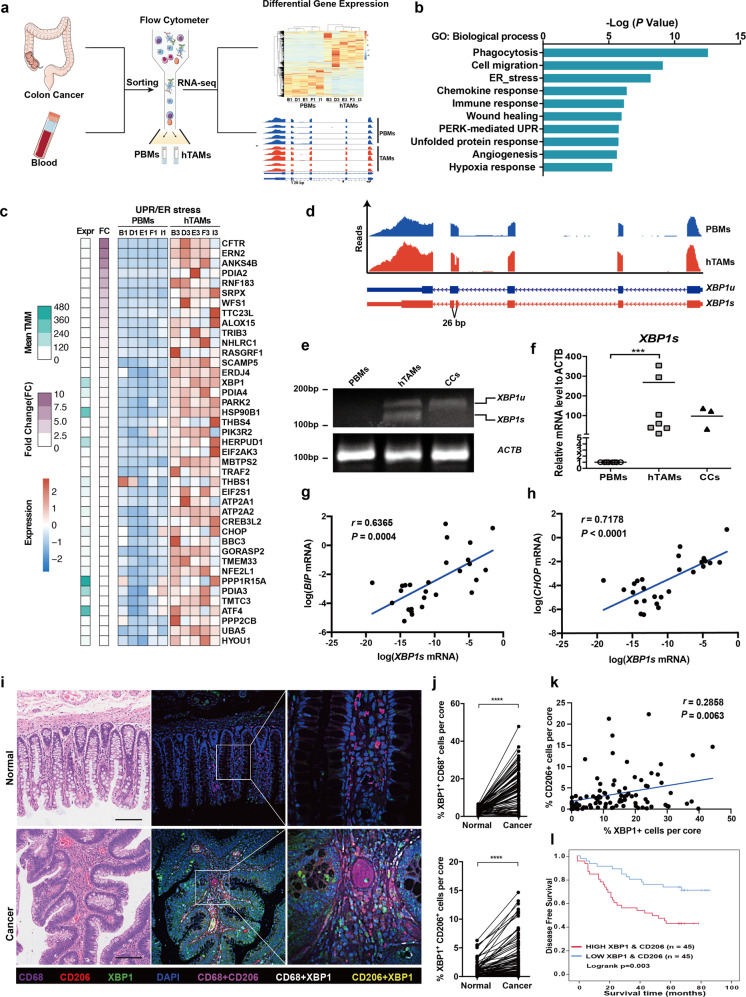
Fig. 1.
UPR/ER-XBP1 activation in human TAMs infiltrate into CRC. a Schematic overview of the strategy for identification of UPR/ER-XBP1 signaling pathways in hTAMs of CRC. b Gene Ontology (GO) term analysis of differentially regulated genes, as revealed using RNA-seq, in five paired hTAMs/PBMs samples. c Upregulation of genes involved in the UPR/ER stress response process. d XBP1 splicing in hTAMs confirmed by RNA-seq alternative mRNA splicing analysis. XBP1u, unspliced form; XBP1s, spliced form. e Detection of XBP1 splicing using conventional RT-PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis. f Expression of XBP1s in PBMs, hTAMs and cancer cells evaluated by RT-qPCR. Data were normalized to endogenous levels of ACTB. ***P < 0.001; ANOVA test. g, h Expression of BIP and CHOP versus XBP1s in all hTAM samples from CRC patients (n = 27). r Spearman’s rank correlation test. i CD206, CD68, and XBP1 immunofluorescence stains in human CRCs and adjacent normal tissues. Scale bar: 100 μm. j XBP1+ CD68+ cells (upper panel), and XBP1+ CD206+ cells (lower panel) among the total number of cells in each individual core from human CRCs and adjacent normal tissues, as determined by PerkingElmer inFormTM system. ****P < 0.0001; paired t-test. k Correlation of percentage of XBP1+ cells with CD206+ in CRC patients. r, Spearman’s rank correlation test. l Kaplan–Meier survival curves for 90 CRC patients with or without high XBP1+CD206+ cells