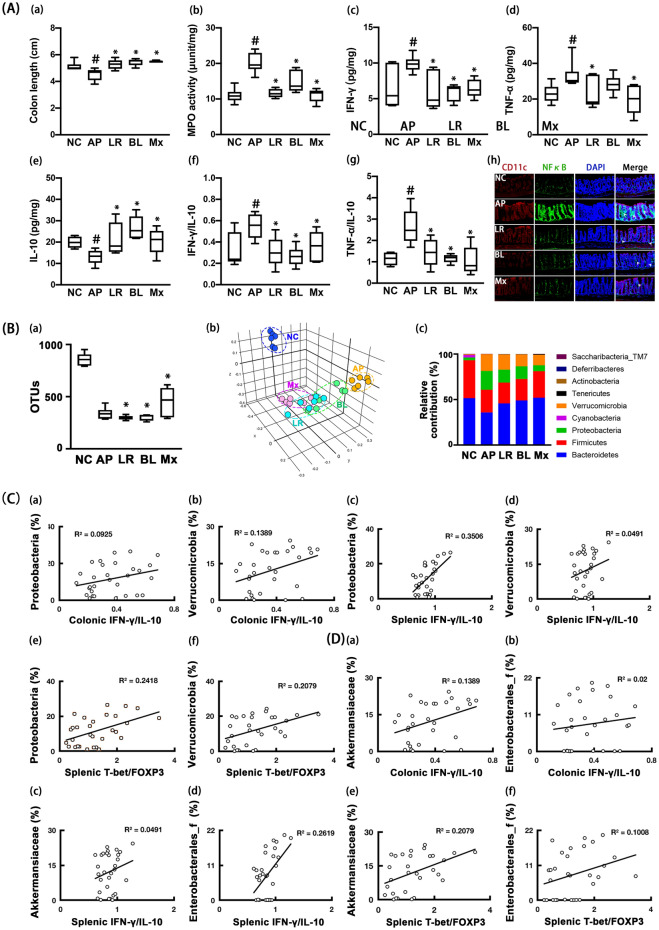
Figure 4.
Effects of NK210 and NK219 on ampicillin-induced gut dysbiosis and inflammation in mice. (A) Effects on colitis: colon length (a), myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity (b), IFN-γ (c), TNF-α (d), IL-10 expression (e), IFN-γ to IL-10 expression ratio (f), TNF-α to IL-10 expression ratio (g), and NF-κB+/CD11c+ cell population in the colon (h). (B) Effects on the gut microbiota composition: (a) α-diversity (OUT richness, a), (b) β-diversity (PCoA plot based on Jensen-Shannon analysis), and (c) gut microbiota composition at the phylum level. The correlation between gut microbiota and IFN-γ to IL-10 or Tbet to Foxp3 expression ratio at the phylum (C) and family levels (D). Test agents (AP, ampicillin alone; LR, 1 × 109 CFU/mouse/day of NK210; BL, 1 × 109 CFU/mouse/day of NK219; Mx, 1 × 109 CFU/mouse/day of LR and BL [4:1] mix) were orally gavaged daily for 5 days after oral gavage of ampicillin. Normal control mice (NC) were treated with vehicle (saline) instead of test agents. Data values indicate mean ± SD (n = 8). #p < 0.05 versus NC group. *p < 0.05 versus AP group treated with ampicillin alone.