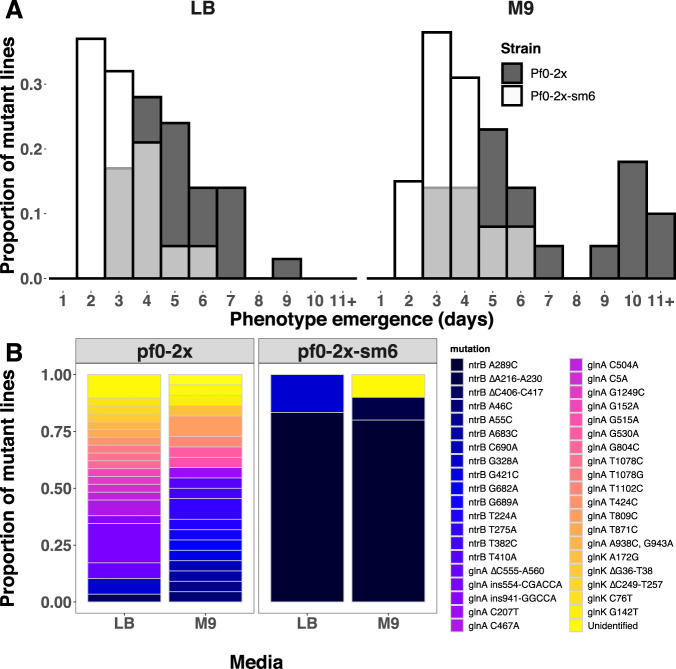
Fig. 5. A synonymous sequence mutant (Pf0-2x-sm) confers a gain of repeatable evolution.
A Histogram of motility phenotype emergence times across independent replicates of an immotile variant of P. fluorescens strain Pf0-1 (Pf0-2x33,grey) and a Pf0-2x strain with six synonymous substitutions in the ntrB locus (Pf0-2x-sm6, white) in two nutrient conditions. B Observed mutational targets following directed evolution of synonymous variants, performed across two environments. Each unique mutation is highlighted by an identifiable colour. (Sample sizes (N): Pf0-2x: LB N = 29, M9 N = 22; Pf0-2x-sm: LB N = 6, M9 N = 10). Unidentified mutations could not be distinguished from wild type sequences of genes belonging to the nitrogen regulatory pathway (ntrB, glnK and glnA) which were analysed by Sanger sequencing. Mutation ntrB A289C was not observed in a single instance in evolved Pf0-2x lines but became the strongly preferred target following synonymous substitution. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.