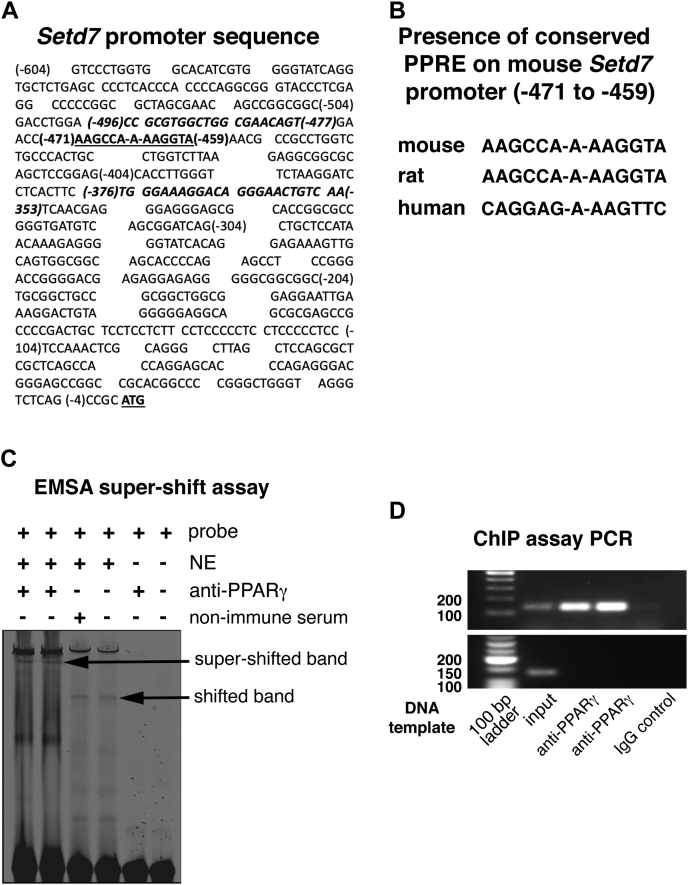
Figure 1.
Nuclear binding assays.A, a partial SetD7 mouse promoter sequence curated using NM_080,793 as DNA reference sequence. The SetD7 PPRE sequence is bolded and underlined. The DNA sequences used for the primers designed for the ChIP assay PCR are bolded and italicized. B, consensus PPRE sequence on the SetD7 promoter: A putative PPARγ response element was found using MatInspector software on the SetD7 promoter region that was conserved between mouse, rat, and human SetD7 promoter sequences. C, EMSA and super-shift assay of SetD7 PPRE: PAGE purified infrared dye (IRD-700) tagged oligos for SetD7 PPRE were annealed and EMSA was performed using nuclear extracts prepared from INS-1 cells as detailed in the Experimental procedures section. For the super-shift assay, INS-1 cell nuclear extracts were preincubated with a PPARγ specific antibody or mouse nonimmune serum on ice for 30 min before adding infrared dye (IRD-700) tagged oligos for SetD7 PPRE. D, upper panel, ChIP assay PCR showing 144 base pairs (bp) SetD7 PPRE positive band: 300–400 bp chromatin preparations of βTC6 cells were prepared as described in the Experimental procedures section. The prepared chromatin samples were immunoprecipitated using anti-PPARγ versus a control nonimmune IgG, followed by PCR of the immunoprecipitated and nonimmunoprecipitated DNA (input DNA) using flanking primer pairs to the mouse SetD7-PPRE. The shown representative bands are the 144 bp (expected length) PCR product from two separate chromatin preparations (out of three independent analysis), along with absence of PCR product in the control mouse IgG lane. D, lower panel, ChIP assay PCR run with input DNA and digested chromatin precipitated with PPARγ specific antibody using primer pairs 800 bp from the SetD7 PPRE with expected PCR product of 129 bp length. The data presented showing the PCR product with input DNA, but the absence in digested chromatin precipitated with PPARγ specific antibody or mouse IgG, thus confirming the fidelity of the ChIP assay PCR in terms of target specificity.