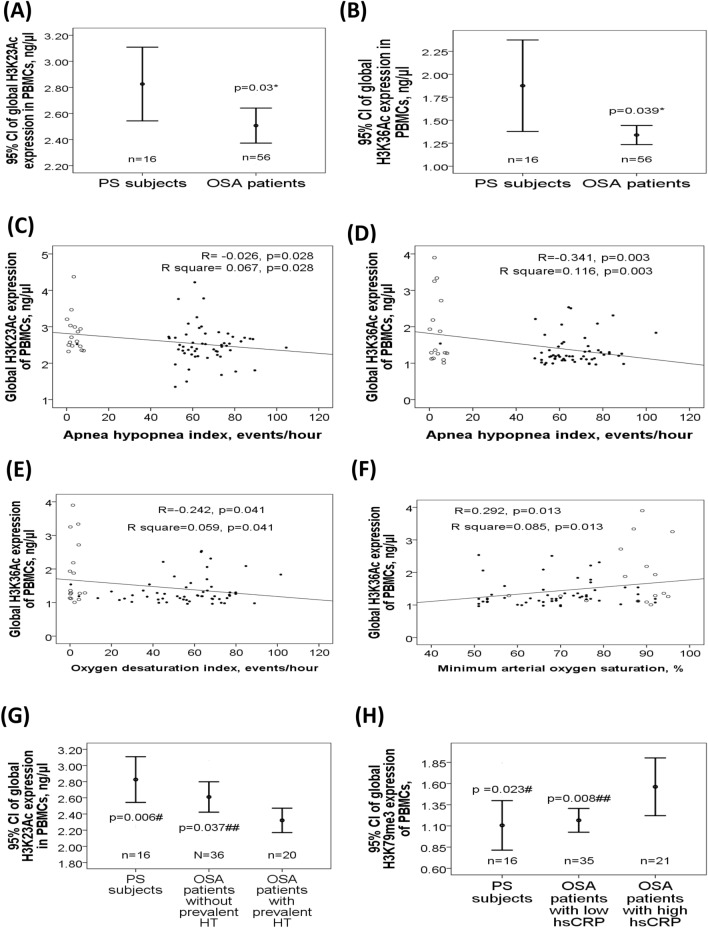
Figure 1.
Differential global histone methylation/acetylation patterns related to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and its clinical phenotypes. Both (A) global histone H3K23Ac and (B) H3K36 Ac expressions were decreased in OSA patients. (C) H3K23Ac expression was negatively correlated with apnea hypopnea index (AHI). H3K36Ac expression was negatively correlated with both (D) AHI and (E) oxygen desaturation index (ODI), and positively with (F) minimum oxygen saturation (SaO2). (G) H3K23Ac expression was further decreased in OSA patients with prevalent hypertension. (H) H3K79me3 expression was increased in OSA patients with high serum hypersensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) levels. *adjust for age, body mass index, gender, smoking history, alcoholism history, and co-morbidities (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, stroke, cardiac disease, chronic kidney disease) by multivariate linear regression analysis. #compared between primary snoring (PS) subjects and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) patients with a particular phenotype (hypertension or high hsCRP), adjusted by multivariate linear regression analysis. ##compared between OSA patients with a particular phenotype (hypertension or high hsCRP) and those without the phenotype, adjusted by multivariate linear regression analysis. Hollow circle indicates PS subjects; solid star indicates OSA patients. PBMC = peripheral blood mononuclear cell; CI = confidence interval; HT = hypertension.