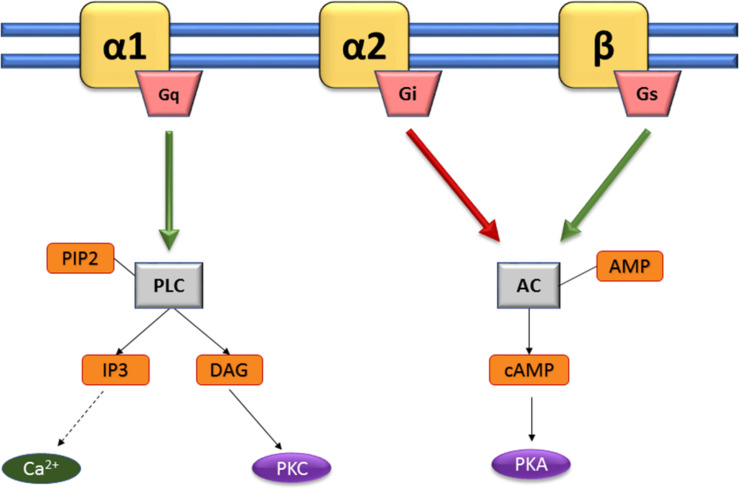
FIGURE 2.
Activating pathways of adrenergic sensors. Catecholamines activate various cellular signal transduction by binding to α 1-, α 2-, and β-adrenoreceptors (yellow). The α1-receptor is coupled with Gq protein, allowing activation of kinase protein C (PKC) and increase of intracellular concentration of Ca2+, through the triphosphate inositol (IP3)/diacylglycerol (DAG) pathway. Activation of this pathway results from the cleavage of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) in IP3 and DAG thanks to phospholipase C (PLC). α-2 and β-receptors are coupled to Gi and Gs, respectively. In both cases, cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is increased or decreased depending on the stimulation (Gs) or inhibition (Gi) of adenylate cyclase (AC), leading to the activation of kinase protein A (PKA). Adapted from Andreis and Singer (2016).