Figure 1.
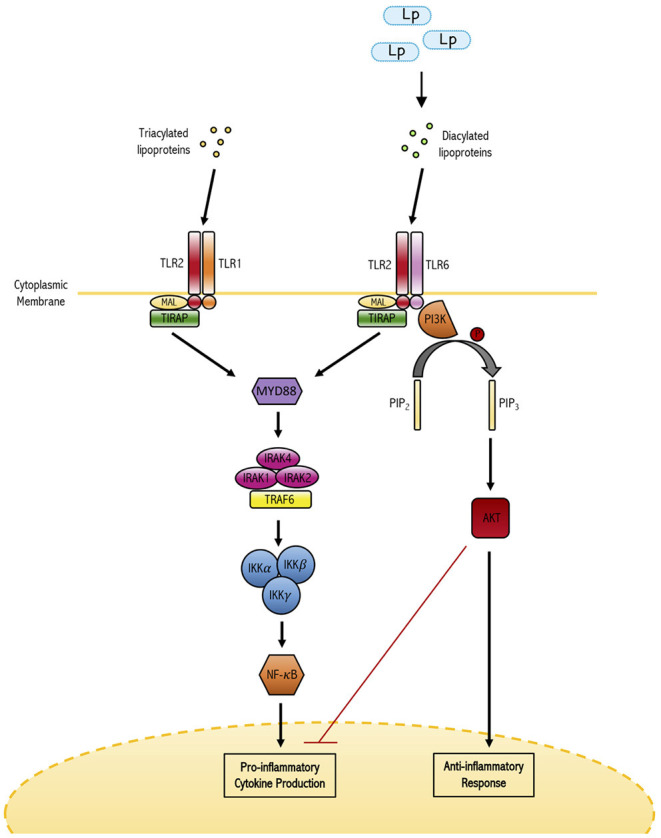
The dual role of TLR-2 in maintaining immune homeostasis. TLR-2 has the capacity to form heterodimers with either TLR-1 or TLR-6. TLRl/2 heterodimers have been shown to bind triacylated lipoproteins frequently derived from gram-negative bacterial species and induce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. On the other hand, the TLR2/6 heterodimer binds diacylated lipoproteins derived from gram-positive bacteria (such as L. plantarum) and induces anti-inflammatory responses. In this way, TLR-2 signaling plays a major role in differential responses to commensal and potentially pathogenic bacteria.
