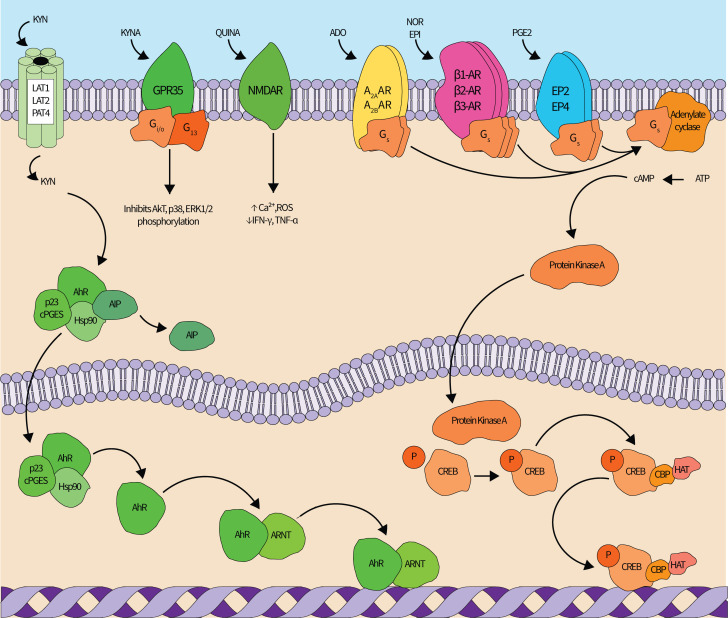
Figure 2.
The redundant signaling networks of immunosuppressive metabolites. Kynurenine (KYN) pathway (left—green): KYN enters the cell via the LAT1, LAT2 or PAT4 transporters. In the cytoplasm, KYN binds the AhR-cPGES-Hsp90-AIP complex. AIP dissociates from the complex after KYN binds, and the KYN-AhR-cPGES-Hsp90 complex translocates into the nucleus. within the nucleus, cPGES and Hsp90 dissociate, and AhR forms a heterodimer with Arnt that modulates gene expression in a widespread manner. Kynurenic acid (KYNA) also agonizes the extracellular GPR35 receptor, which inhibits Akt, p38, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation, and quinolinic acid (QUINA) agonizes the NMDA receptors to increase intracellular Ca2+ and ROS and decrease IFN-γ and TNF-α production. Adenosine (ADO) (top center left—yellow): ADO can agonize four different G-protein coupled receptors (GPR35), of which A2AAR and A2BAR stimulate cAMP generation and downstream immunosuppression mediated by the cAMP-PKA-CREB pathway, shown in orange. (Nor)epinephrine (NOR) (top center right—magenta): NOR and epinephrine (EPI) can agonize either α-adrenergic or β-adrenergic receptors (β-AR). Agonism of all three β-AR elicits immunosuppressive signaling cascades through cAMP-PKA-CREB. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (top rightadrenergic—blue): similar to ADO, PGE2 can agonize four receptors, of which two (EP2 and EP4) elicit immunosuppressive signaling cascades through cAMP-PKA-CREB. cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling pathway: cAMP production is increased by ADO, NOR, and/or PGE2 signaling through Gs-mediated activation of adenylate cyclase. adenylate cyclase generates cAMP from ATP, and cAMP then activates PKA. A cAMP-PKA complex enters the nucleus where it phosphorylates the CREB transcription factor. phosphorylated CREB recruits HAT and CBP and then modulates target gene expression. All proteins are denoted by text within shapes while metabolites are free-floating text. Straight lines indicate an enzyme catalyzed reaction while curved lines indicate transport or are included for clarity. AXAR, adenosine receptor; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; AIP, aryl hydrocarbon receptor-interacting protein; ARNT, aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; Ca2+, calcium ion; cAMP, cyclic AMP; CBP, CREB binding protein; cPGES, cytosolic PGE synthase; CREB, cAMP-response element binding protein; EPX, PGE2 receptor; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GX, protein G; HAT, histone acetyltransferase; Hsp, heat shock protein; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; LAT, L-type/large neutral amino acid transporter; NMDAR, N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor; P, phosphate group; PAT, proton-assisted amino acid transporter; ROS, reactive oxidative species; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha.