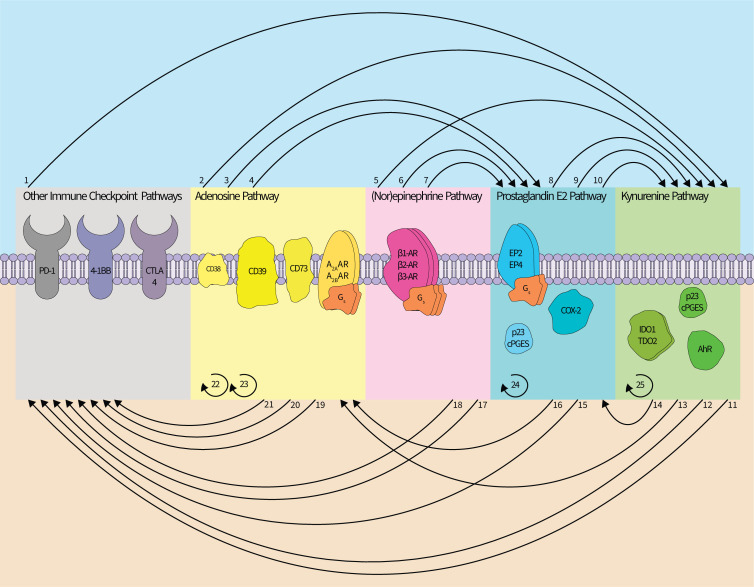
Figure 3.
Interactions within and between the immunosuppressive metabolite networks. The adenosine (ADO), kynurenine, (PGE2), (nor)epinephrine (NOR), and other immune checkpoint pathways interact and stimulate each other and may employ feedforward signaling/synthesis regimes. (1) Blockade of PD-1 or CTLA-4 appears to induce (IDO1) expression. (2) A2BAR signaling induces (IDO1) expression. (3, 4) CD39 and CD73 can promote synthesis of (PGE2), and A2AAR or A2BAR signaling can induce expression of COX-2. (5) β-AR signaling upregulates (IDO1) expression. (6, 7) β2-AR signaling has been linked to the upregulation of COX-2 and cPGES. (8, 9, 10) cPGES is a modulator of (AhR) activity, and COX-2 can influence expression of (TDO2) and (IDO1). (11, 12) (AhR) signaling can increase PD-1 expression and correlates with reduced efficacy of an αCTLA-4 antibody. (13) (AhR) signaling can promote expression of (CD39.) (14) (AhR) signaling can promote expression of COX-2. (15) EP2/4 signaling can increase PD-1 expression. (16) (PGE2) can induce expression of CD73.) (17, 18) β-adrenergic signaling correlates with diminished therapeutic efficacy of αPD-1 antibodies, and decreases the therapeutic efficacy of a 4-1BB blockade. (19, 20) (CD73) expression correlates with diminished therapeutic efficacy of αPD-1 antibodies and of an αCTLA-4 antibody. (21) CD38 is associated with tumorous resistance to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody therapy. (22, 23) A2A/BAR signaling drives (CD73) expression, and A2AAR signaling increases (CD39) expression. (24) PGE2-EP2/4 signaling can upregulate COX-2 expression. (25) (AhR) signaling drives upregulation of (IDO1) expression. In total, direct links between each pathway have been described with the exception of a relationship between ADO and NOR. Colors denoting ADO, kynurenine, (PGE2), and NOR pathways follow (figures 1 and 2). For brevity, the distinct cell types in which these interactions were described are not included. Curved lines between pathways indicate an interpathway interaction whereas curved semicircles indicate intrapathway regulation. AXAR, adenosine receptor; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; β-AR, β-adrenergic receptor; CD, cluster of differentiation; COX, cyclooxygenase; cPGES, cytosolic prostaglandin E synthase; CTLA, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein; EPI, epinephrine; PGE receptorIDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; PD, programmed cell death receptor; TDO, tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase.