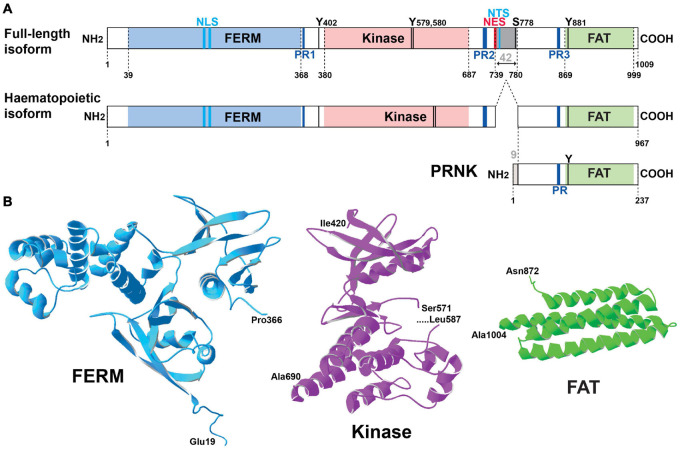
FIGURE 1.
Pyk2 structure. (A) Schematic representation of Pyk2 protein isoforms. The limits of the structural domains are indicated with the first and last residue (numbering of mouse Pyk2): FERM, 4.1-ezrin-radixin-moesin, FAT, focal adhesion targeting. A Pyk2 protein isoform observed in cells of the hematopoietic lineage results from alternative splicing with the absence of an exon coding 42-amino acids (gray box). PRNK (Pyk2-related non-kinase) is a short isoform that derives from transcription initiation at an internal promoter and consists of the C-terminal region of Pyk2 with 9 additional residues at its N-terminus that are not found in Pyk2. Other important sites are indicated including the main characterized phosphorylation sites (T, threonine, Y, tyrosine), the proline-rich motifs (PR), the nuclear localization sequence (NLS), nuclear export sequence (NES), and nuclear targeting sequence (NTS). See text for references. (B) Three-dimensional structure of the main domains of Pyk2 for which the crystal structure has been determined. The structures were drawn with Deep View/Swiss Pdb viewer (http://www.expasy.org/spdbv/) for the FERM (pdb4eku), kinase (pdb4h1m), and FAT (pdb4gm3) domains.