Figure 2.
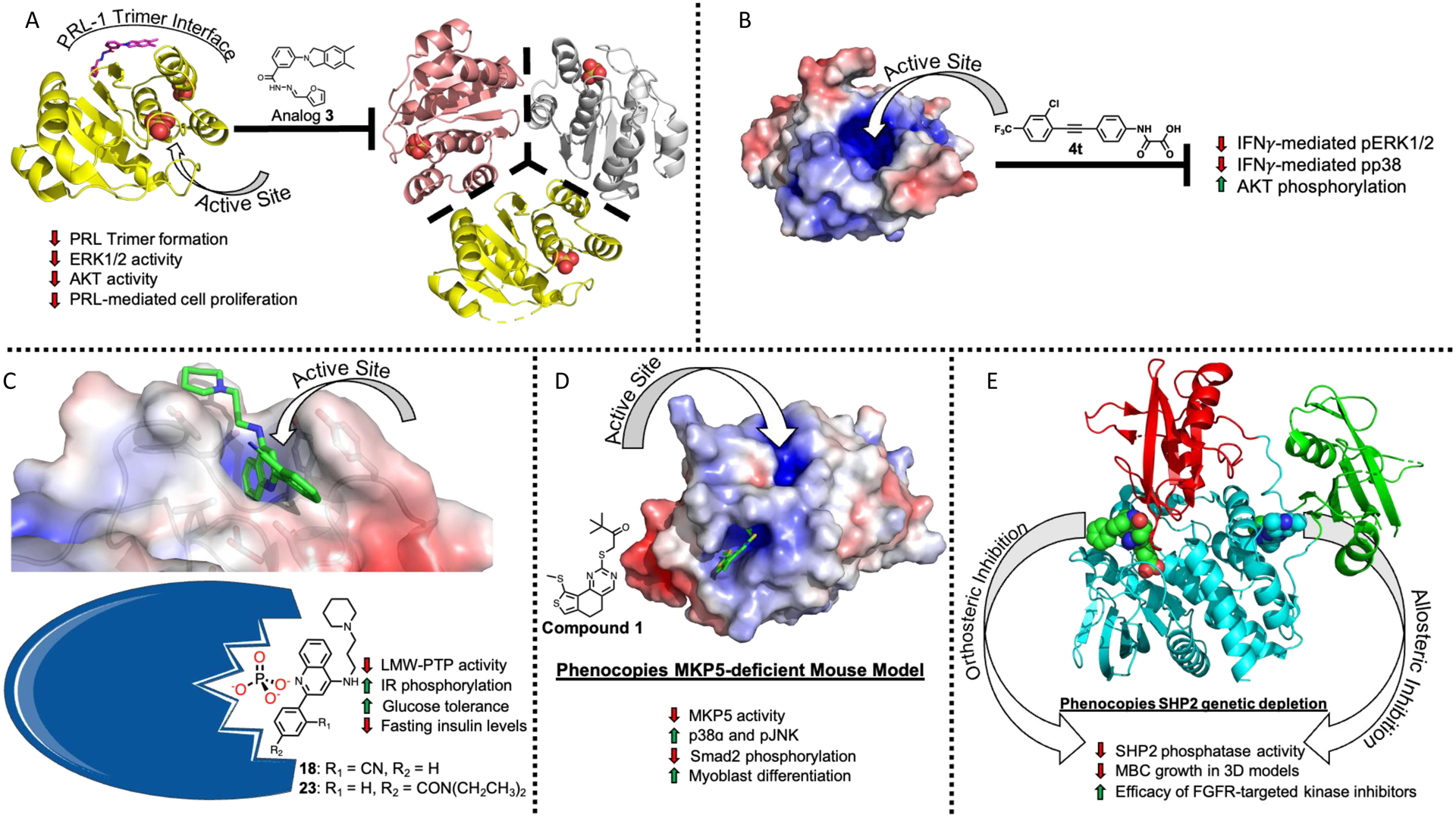
A) Analog 3 (magenta sticks) (PDB ID 5BX1) and Cmpd 43 (not shown) both prevent PRL-1 (yellow) from forming a homotrimer, resulting in decreased ERK1/2 activity, decreased AKT activity, and decreased cell proliferation. B) Inhibition of mPTPB by compound 4t prevents the interferon gamma (IFNγ) mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 and increase AKT phosphorylation. C) Uncompetitive inhibitor 18 (green sticks) reduces phosphatase activity of LMW-PTP (Cartoon depiction adapted from Servier Medical Art under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0), resulting in increased insulin receptor (IR) phosphorylation, increased glucose tolerance, and decreased fasting insulin levels, linking LMW-PTP activity to diabetes. D) Allosteric inhibition of MPK5 by compound 1 (green sticks) results in decreased MPK5 activity and increased levels of p38ɑ and pJNK, leading to decreased Smad2 phosphorylation levels and increased myoblast differentiation. E) Active site inhibitors (green spheres) and allosteric inhibition (blue spheres) phenocopy genetic depletion of SHP2, decreasing growth of metastatic breast cancer tumors in 3D models and increasing efficacy of FGFR-targeted kinase inhibitors.
