Figure 3. d11-associated enhancement of infectivity in an HBV/NL system.
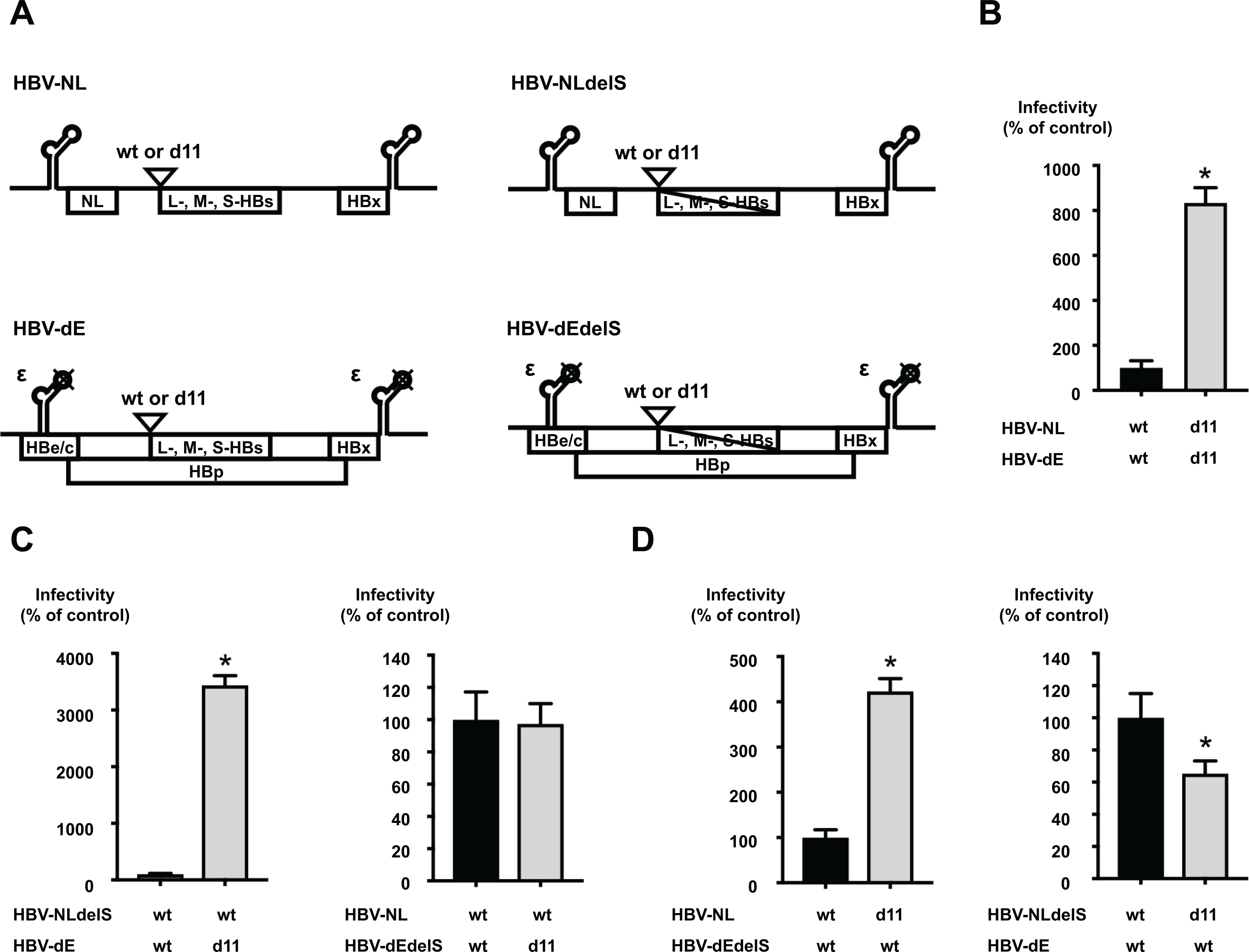
(A) The structure of plasmids for HBV/NL used in this study. The constructs of the encapsidation competent-reporter plasmid (HBV-NL-wt) and the encapsidation incompetent-plasmid (HBV-dE-wt) were prepared. The d11 was introduced to these plasmids and designated HBV-NL-d11 and HBV-dE-d11, respectively. The substitutions of the start codons of L-, M-, and S-HBs was also introduced to these plasmids and generated HBV-NLdelS-wt, HBV-NLdelS-d11, HBV-dEdelS-wt, and HBV-dEdelS-d11. NL; NanoLuc. (B) Infection of reporter HBV generated by transfection of HBV/NL plasmids with or without d11. The generated HBV/NL was quantified after DNase treatment and inoculated onto HepG2/NTCP-18C cells at 3 GEq/cell. After 8 days of incubation, infected cells were lysed, and the NL activities were measured. Infectivity of the virus with d11 is represented as the percentage of infectivity of the virus without d11. (C) Assessment of the effects of d11 in the L-HBs and HBp proteins. The HBV reporter generated by the transfection of the indicated plasmids was inoculated at 50 GEq/cell. The infectivity of the virus with d11 is represented as the percentage of infectivity of the virus without d11. (D) Assessment of the effects of d11 in the L-HBs protein and packaged genome length. The HBV reporter generated by the transfection of the indicated plasmids was inoculated at 50 GEq/cell. The infectivity of the virus with d11 is represented as the percentage of infectivity of the virus without d11. The data are indicated as the mean ± standard deviation of the quintuplicate assay. Asterisk indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05).
