Figure 6.
NSP9 inhibits the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of STAT1 in a SETD2-dependent manner
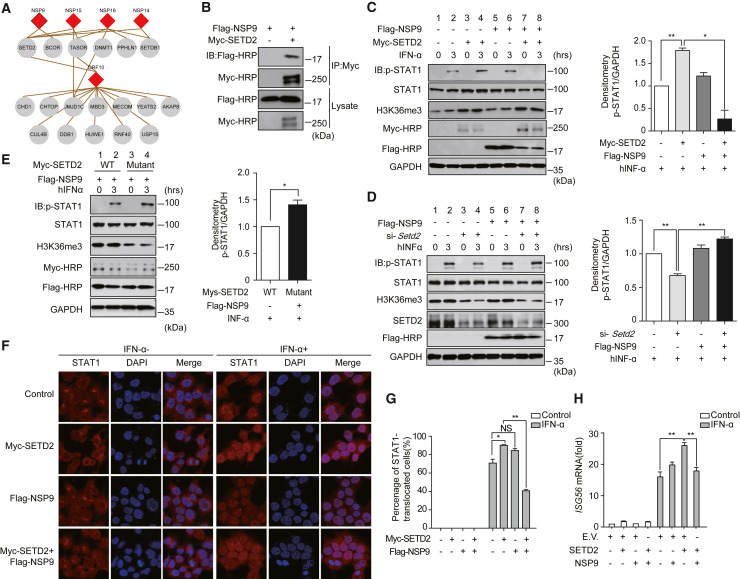
(A) Epigenetic regulators associated with viral proteins.
(B) Validation of the interactions of NSP9 and SETD2 by co-immunoprecipitation assay.
(C) HEK293T cells were treated with hIFN-α (10 ng/mL). Phosphorylated STAT1, SETD2, and H3K36me3 in HEK293T cells were detected by the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Quantitative analysis of p-STAT1 is shown.
(D) p-STAT1, STAT1, H3K36me3, and SETD2 were detected in HEK293T cells. The cells were transfected with si-Control or si-Setd2 together with empty vector or FLAG-NSP9 and stimulated as in (C). Quantitative analysis of p-STAT1 is shown.
(E) p-STAT1, STAT1, and H3K36me3 were detected in HEK293T cells co-transfected with Myc-tagged SETD2 or mutated SETD2 and FLAG-NSP9, followed by hIFN-α treatment as in (C). Quantitative analysis of p-STAT1 is shown.
(F) The nuclear translocation of STAT1 was visualized by confocal microscopy. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated vectors for 24 h, followed by hIFN-α (10 ng/mL) treatment for 30 min or untreated. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(G) Quantitation of the nuclear translocation of STAT1.
(H) HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. hIFN-α was used to stimulate the activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. The cells were harvested for RNA isolation. The induction of ISG56 was evaluated by RT-qPCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control. The fold changes were quantified by the 2−ΔΔCt method.
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.001; NS, not significant (two-tailed Student's t test), means +SD, n = 2 (C–E) or n = 3 (G and H). Data are representative of two (B–E) or three (F–H) independent experiments. E.V., empty vector.