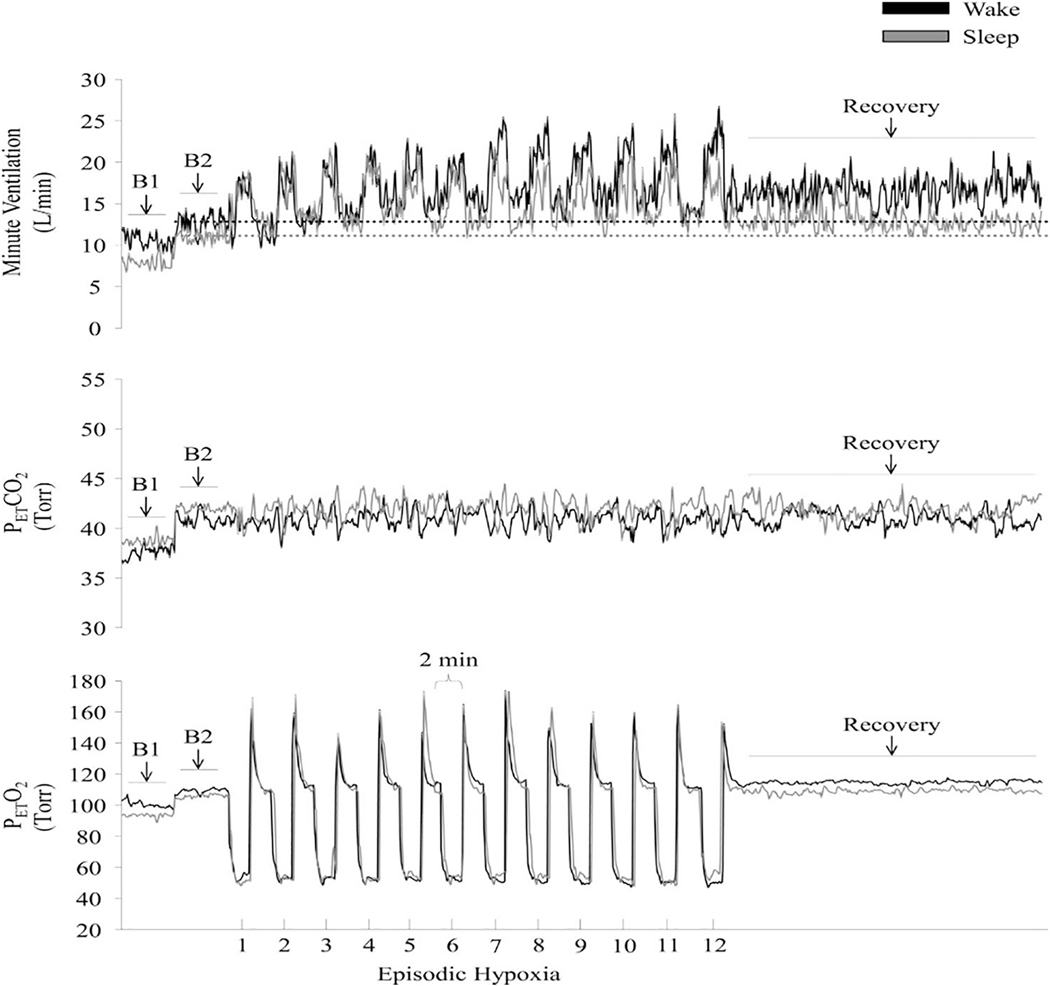
Fig. 4.
Measures of minute ventilation (top), PETCO2 (middle), and PETO2 (bottom) during completion of an intermittent hypoxia protocol during wakefulness and sleep. A raw record of breath-by-breath minute ventilation recorded from one participant exposed to intermittent hypoxia is shown. The dotted lines represent baseline values specific to each state. Note that minute ventilation during the end-recovery period was greater than baseline during wakefulness as well as during sleep. Also note that the magnitude of the increase during recovery compared to baseline was greater during wakefulness compared to sleep. B1, last 5 min of the initial normocapnic 10 min baseline period; B2, last 5 min of the second baseline period during which PETCO2 was elevated 3 Torr above B1 measures. Reprinted from “The impact of arousal state, sex, and sleep apnea on the magnitude of progressive augmentation and ventilatory long-term facilitation” by Z. Syed et al. J. Appl. Physiol. 114: 52–65, 2013.