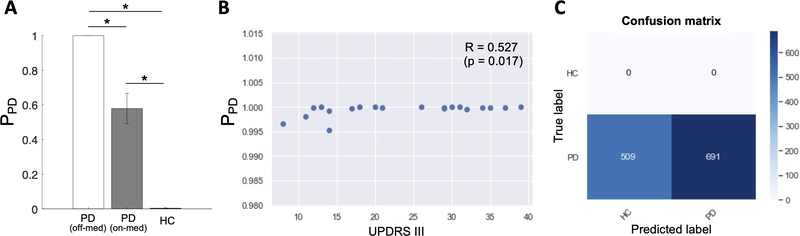
Fig. 4.
(A) The probability of PD (PPD) estimated by the CRNN model for the PD (off- and on- medication) and HC groups. Each bar graph shows the mean and standard deviation of PPD across the participants in each group. P-values from the one-sample (off- vs. on-med) t-test and two-sample t-tests (PD off-med vs. HC; PD on-med vs. HC) are indicated with asterisks (*: Bonferroni-corrected p < 0.001). (B) A scatter plot of the PPD and UPDRS part III scores of the PD participants demonstrates a positive correlation (R = 0.527, p = 0.017). (C) Confusion matrix showing that the CRNN model predicts 509 out of 1200 PD EEG samples as HC when the EEG was recorded an hour after the participants took a regular dose of L-dopa medication.